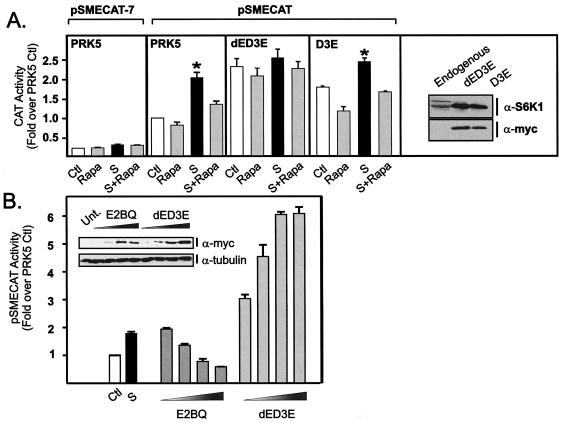
FIG. 2.
S6K1 is necessary and sufficient to regulate rDNA transcription in mammalian cells. (A) NIH 3T3 cells (0.18 × 106 cells/well) were transfected 24 h after plating with the following plasmid constructs: a reporter construct for rDNA transcription (pSMECAT) (0.45 μg), a control vector in which an essential G at position −7 in the 45S promoter was mutated in the control reporter (pSMECAT-7), empty vector PRK5 (0.45 μg), or the indicated S6K1 mutants, dED3E or D3E (0.45 μg). The cells were then transferred into DMEM containing 0.5% BSA. After 24 h of serum starvation, the cells were pretreated with rapamycin (20 nM) or vehicle (ethanol) for 30 min and then stimulated with DMEM plus 10% FBS for a further 24 h before being assayed for CAT activity. Samples were analyzed in parallel for endogenous and recombinant S6K1 expression with an antibody directed to the carboxy-terminal region of S6K1 or the myc tag. (B) Cells were plated and transfected as described above with pSMECAT (0.45 μg) and increasing amounts of the dominant-negative construct E2BQ (0.45, 0.9, 1.8, and 3.6 μg) or dED3E (0.45, 0.9, 1.8, and 3.6 μg) and then transferred into DMEM containing 10% BSA. Total plasmid DNA per transfection was equalized with the empty vector, PRK5. After 48 h, the cells were assayed for CAT activity. Samples were analyzed in parallel for recombinant S6K1 expression (myc) and tubulin as a control for loading (see insert). Values that are significantly different (P < 0.05) from the control values (serum-starved cells) (n = 5) are indicated (*). Abbreviations: Ctl, control; Rapa, 20 nM rapamycin; S, 10% FBS; S+Rapa, 10% FBS plus 20 nM rapamycin; α-S6K1, anti-S6K1; Unt., untransfected.