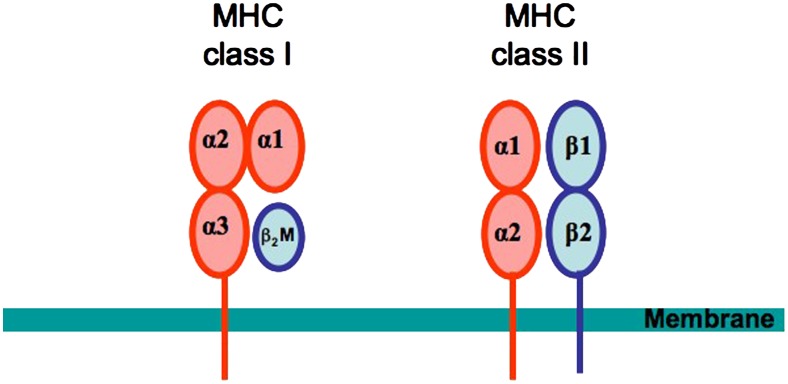
Figure 2.
Structure of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. The MHC class I molecules are composed of a heavy α chain and a light β2-microglobulin chain. The α chain is composed of three extracellular domains (α1, α2, and α3), a transmembrane-spanning domain, and a small cytoplasmic domain. The α1 and α2 domains together form a peptide-binding groove presenting peptide to CD8+ T cells. MHC Class II molecules are heterodimers with an α and a β chain. Both chains have two extracellular domains, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic domain. The α1 and β1 domains together form the peptide-binding groove presenting peptide to CD4+ T cells.