Figure 6.
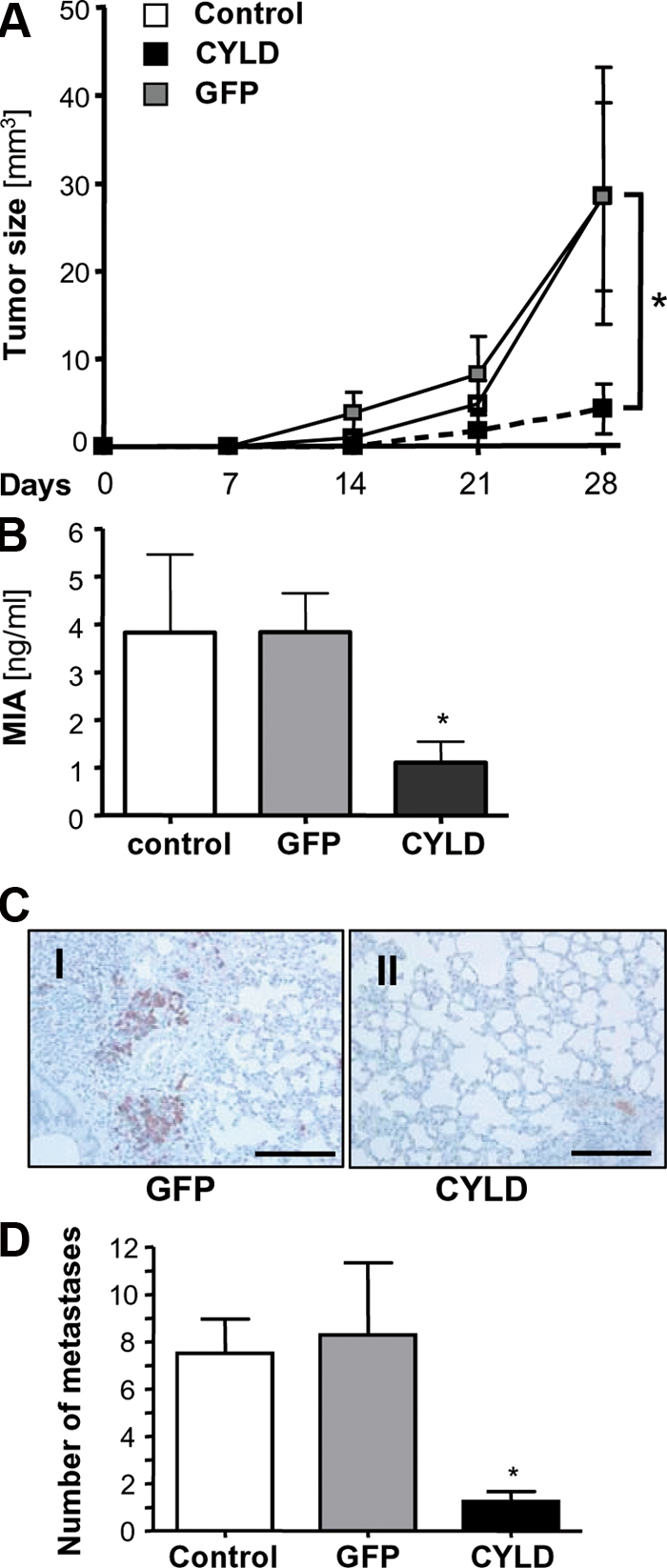
CYLD inhibits proliferation and metastasis of melanoma cells in vivo. (A) Growth kinetic of tumors formed by Mel Im control cells (Control) or cells transduced with viral vectors carrying CYLD or GFP after subcutaneous implantation into nude mice (106 cells/mouse). Data represent mean tumor size (± SEM) at different time points. *, P < 0.05 versus both GFP and Control. (B) MIA serum levels in nude mice after i.v. injection of Mel Im control cells (Control) or cells transduced with viral vectors carrying CYLD or GFP (106 cells/mouse; 8–10 mice/group). Data represent mean MIA level (± SEM) 4 wk after injection. (*, P < 0.05 versus both GFP and Control). (C) Immunohistochemical MART1 staining of pulmonary tissue 4 wk after inoculation. Photomicrographs showing representative sections of the lung of mice receiving Mel Im cells transduced with CYLD or GFP. Bar, 200 μm. (D) Number of micrometastatic lesions per one representative cross section of the lungs from each mouse. Data are given as mean ± SEM. *, P < 0.05 compared with control and GFP. Experiments and analysis in A–D have been performed with 8–10 mice/group.
