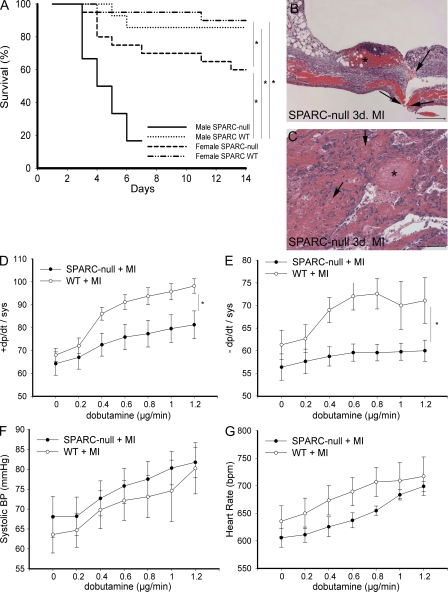
Figure 2.
Absence of SPARC results in cardiac rupture and dysfunction. (A) Kaplan-Meier curve showing that targeted deletion of SPARC resulted in decreased survival of SPARC-null (mainly male) compared with WT mice after MI (*, P < 0.05). Decreased survival was mainly caused by cardiac rupture. Two male SPARC-null mice had to be killed at 7 d after MI because of severe shortness of breath and, therefore, were not included in the survival curve. (B and C) Histological analysis of ruptured LV of male SPARC-null infarcted hearts (hematoxylin and eosin stained) revealing rupture site (B, arrows), intramural hemorrhages of the infarcted ventricular wall (C, arrows), and massive infiltration of erythrocytes and inflammatory cells (C) and thrombi (B and C, asterisks) at 3 d after MI. (D–G) Decreased survival is associated with depressed cardiac contractility (D) and relaxation (E) during infusion of dobutamine in SPARC-null female (n = 7) in comparison with female WT (n = 9) mice 14 d after MI, whereas systolic blood pressure (BP; F) and heart rate (G) did not differ significantly (*, P < 0.05). bpm, beats per minute. Error bars represent the mean ± SEM. Bars: (B) 200 μm; (C) 100 μm.