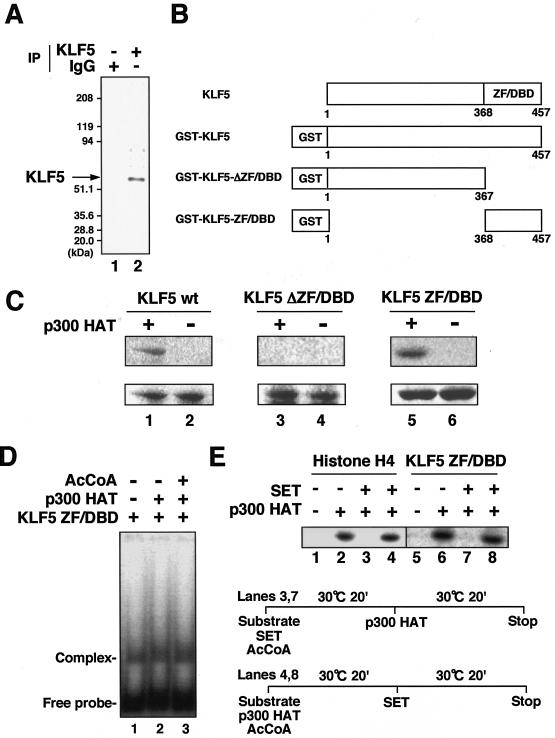
FIG. 4.
Acetylation of KLF5 and its regulation by SET. (A) Acetylation of KLF5 in vivo. Cells were treated with trichostatin A and labeled with [3H]acetate followed by immunoprecipitation with KLF5 (lane 2) and control normal IgG antibodies (lane 1). (B) Schematic representation of GST-KLF5 fusion mutant constructs. GST-KLF5 comprises full-length KLF5 fused to GST, GST-KLF5-ΔZF/DBD comprises only the N-terminal regulatory domain fused to GST, and GST-KLF5-ZF/DBD comprises only the C-terminal zinc finger DBD fused to GST. (C) Acetylation of KLF5 mutant constructs in vitro by p300. KLF5 proteins (1.2 μg) were incubated with 50 ng of FLAG-p300 HAT domain protein (amino acids 1195 to 1673) in the presence of [14C]acetyl-CoA. Reaction products were separated by SDS-12% PAGE. The difference between pairs (lanes 1 and 2, 3 and 4, and 5 and 6) is the presence of p300 HAT protein in the reaction mixture for the respective KLF5 mutant proteins. The gel was stained with Coomassie brilliant blue (lower panel) and then analyzed with a BAS 1500 phosphorimager (upper panel). (D) Effects of acetylation on KLF5 DNA-binding activity. Acetylation reactions were performed in the presence (+) of acetyl-CoA (AcCoA) and FLAG-p300 HAT domain (lane 3), in the presence of FLAG-p300 HAT domain (lane 2), and in the absence (−) of acetyl-CoA or FLAG-p300 HAT domain (lane 1). Reaction products were resolved by electrophoresis and analyzed with BAS1500. (E) Effects of SET on KLF5 acetylation (lanes 5 to 8). Histone H4 was used as a control (lanes 1 to 4). A schematic diagram of the protocol for order-of-addition experiments is shown. In lanes 3 and 7, the p300 HAT domain was added following the reaction of SET with the substrate (KLF5 ZF/DBD or histone H4) (prior to acetylation), and in lanes 4 and 8, SET was added following the reaction of p300 HAT with the substrate (after acetylation). Acetylation reactions were done essentially as described above. All experiments were done at least twice with consistent findings.