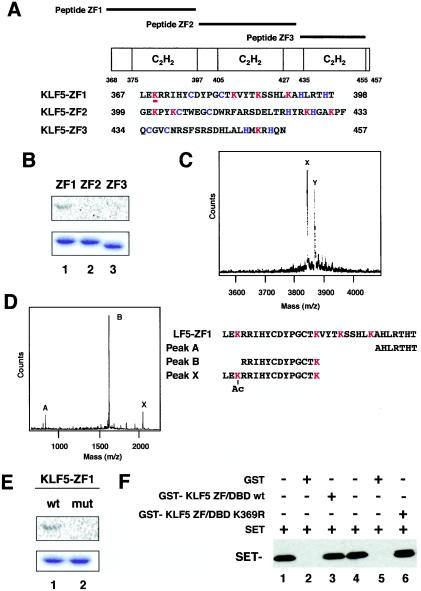
FIG. 6.
Mapping of the acetylated region and residue of KLF5. (A) Schematic representation of KLF5 zinc finger peptides. ZF1, ZF2, and ZF3 cover each of the zinc fingers, respectively, from the N terminus. (B) Acetylation of KLF5 zinc finger mutants in vitro. Approximately 1.0 μg of purified GST-KLF5 fusion zinc fingers 1, 2, and 3 were incubated with [14C]acetyl-CoA and recombinant FLAG-p300 HAT domain. Reaction products were separated by SDS-10% PAGE. The gel was stained with Coomassie brilliant blue (lower panel) and then analyzed with a BAS 1500 phosphorimager (upper panel). (C) Mass spectrum quantification of acetylated lysines in peptide KLF5-ZF1. A parallel reaction mixture with unlabeled acetyl-CoA was analyzed by MALDI-TOF (MS). The major peak labeled X corresponds to the expected mass of the unmodified peptide KLF5-ZF1. The major peak labeled Y, larger by 42 atomic mass units, represents monoacetylated peptide. (D) Masses of peptides digested withLys-C endopeptidase. The peptide sequences that are suggested from measured masses are shown below. Peak X represents the acetylated fragment. (E) Replacement of acetylated lysine by arginine impairs acetylation of GST-KLF5-zinc finger 1. Approximately 1.0 μg of purified GST-KLF5-zinc finger 1 (lane 1, wild type [wt]) and GST-KLF5-mut zinc finger 1 (K369R) (lane 2, mutant [mut]) were incubated with [14C]acetyl-CoA and 50 ng of FLAG-p300 HAT domain protein. Reaction products were separated by SDS-10% PAGE. The gel was stained with Coomassie brilliant blue (lower panel) and then analyzed with a BAS 1500 phosphorimager (upper panel). (F) Binding assay of K369R and wild-type KLF5 with SET. Wild-type and K369R mutant KLF5 fused to GST were immobilized on GST resin followed by a pull-down assay of SET protein. Lanes 1 and 4 are SET input. Lanes 2 and 5 are GST alone. All experiments were done at least twice with consistent findings. +, present; −, absent.