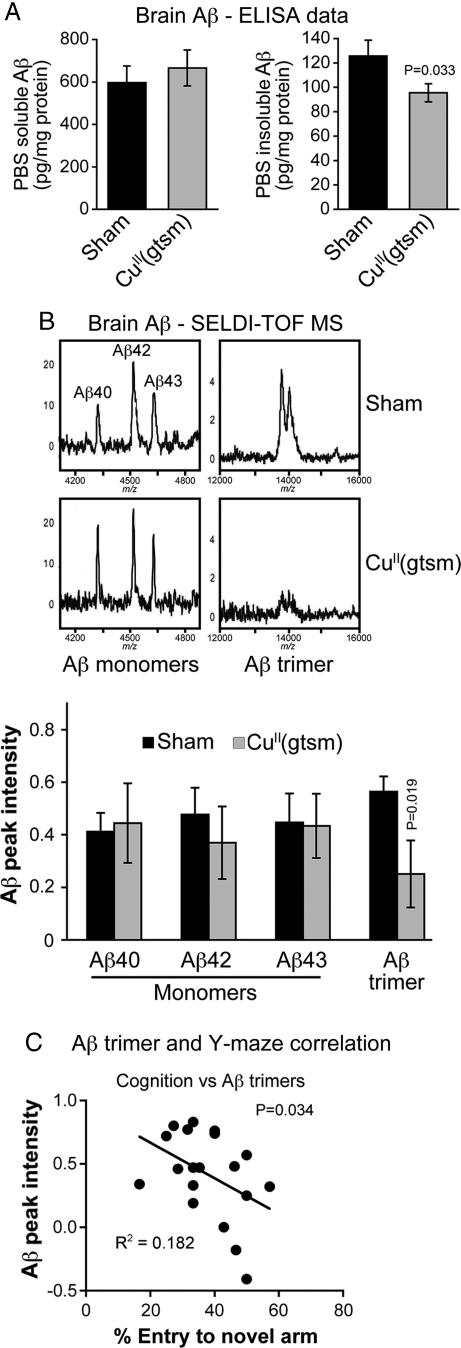
Fig. 5.
CuII(gtsm) inhibits accumulation of PBS insoluble Aβ trimers in the brains of AD mice. (A) ELISA data showing that overall levels of PBS insoluble Aβ, but not PBS soluble Aβ, are decreased in the brains of CuII(gtsm)-treated AD mice. (B) SELDI-TOF MS analysis showing Aβ trimers are decreased in the PBS-insoluble fraction of CuII(gtsm)-treated mice, but monomer levels are unaffected. All SELDI-TOF MS data are normalized for total brain protein and are expressed as Aβ peak intensity per milligram of protein. (C) Correlation analysis showing cognitive performance in Y-maze testing of AD mice improves with decreasing Aβ trimer levels in the PBS-insoluble fraction of the brain. P values shown indicate that treatments induced significant effects compared with the sham control. Data in A and Aβ peak intensity data in B are mean values ± SEM.