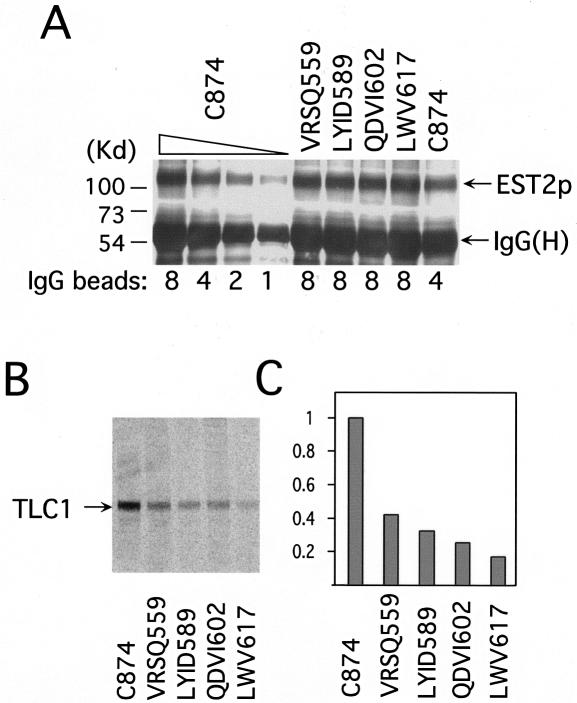
FIG. 3.
Mutations in the IFD region lead to reductions in the level of TERT-associated RNA. (A) Levels of protein A-tagged TERT in the mutant extracts were determined by enrichment on IgG-Sepharose and subsequent Western blotting with antibodies directed against protein A and compared to that of the wild-type extract. The identities of the mutants are indicated at the top, and the relative amounts of beads loaded are indicated at the bottom. The position of the protein A-tagged Est2p and the IgG heavy chain are marked by arrows on the right. (B) The levels of TERT-associated TLC1 RNA in the wild-type and mutant strains were determined by RNase protection assays. The identities of the mutants are indicated at the bottom. The position of the protected TLC1 fragment is indicated by an arrow on the left. (C) The levels of TERT-associated TLC1 RNA in the mutant strains relative to the wild-type strain were determined by assays such as those shown in B, and the average values from two experiments were plotted.