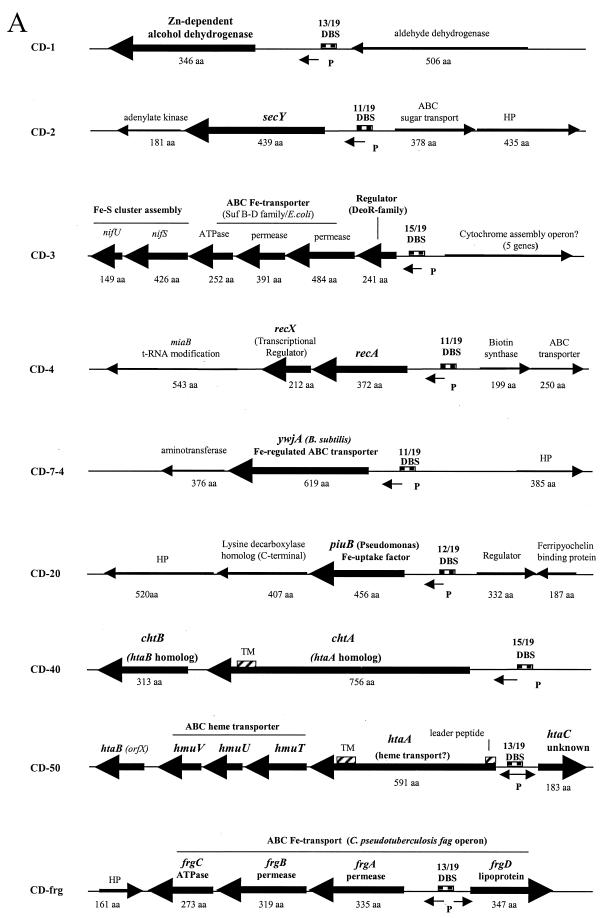
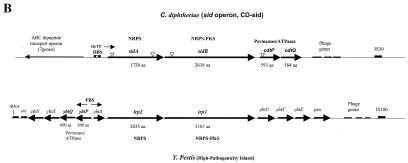
FIG. 2.
(A) Genetic maps showing portions of the C. diphtheriae chromosome that flank the various DtxR binding sites identified by DRTA. The names of the various DRTA clones are indicated to the left of each map. Genes that showed the highest homology to C. diphtheriae ORFs are indicated (obtained from Blast searches of the NCBI database). Arrows indicate direction of transcription, and large arrows indicate ORFs that may be regulated by DtxR and iron. Predicted protein sizes for C. diphtheriae genes are indicated in amino acids (aa). Abbreviations: DBS, DtxR binding sites (matches with the 19-bp consensus sequence are shown above each binding site); P, putative promoter elements; TM, putative transmembrane regions in HtaA and ChtA; HP hypothetical protein. (B) Comparison of the sid operon with the Y. pestis HPI. Triangles indicate locations of vector insertion in the various sid operon mutants. Abbreviations: PKS, polyketide synthase; NRPS, nonribosomal peptide synthetase; FBS, Fur binding site. Genetic maps are not to scale.