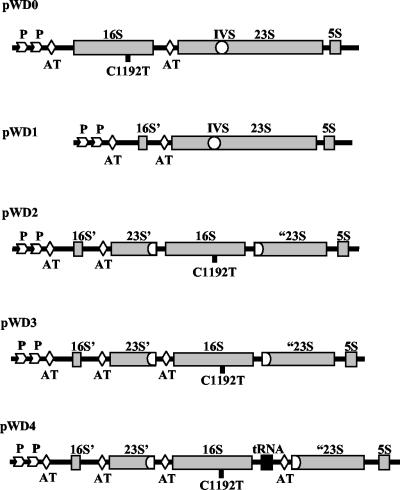
FIG. 1.
Diagram of the constructed rrn operons. pWD0, pKK3535 derivative with a C1192T transition in the 16S gene and an insertion of the IVS element from the S. enterica serovar Typhimurium 23S rDNA gene into helix 45; pWD1, deletion of 1,500 bp of the 1,542-bp 16S gene and most of tRNAGlu2 by use of StuI and XbaI restriction sites; pWD2, a PCR-generated copy of the 16S gene from pWD0, designed with artificial AatII sticky ends, was inserted into the Salmonella IVS at the unique AatII site in pWD1. pWD3 and pWD4 were constructed similarly to pWD2 except that the 5′ and 3′ ends of the PCR fragments differed (see Materials and Methods for details). pWD3 had additional 5′ leader sequences, and pWD4 had tRNAGlu2 and an additional rrn AT sequence from the intergenic spacer region of the rrnB operon. 16S’, 42-bp fragment left after deletion of the 16S gene; 23S’ and “23S, proximal and distal parts of the 23S gene before and after the IVS insertion, respectively.