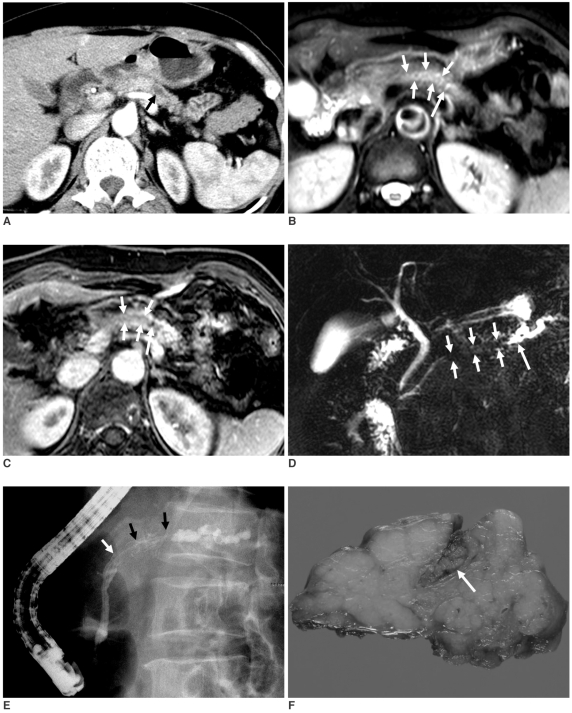
Fig. 1.
63-year-old woman with intraductal tubular carcinoma of pancreas that presented as intraductal mass.
A. Contrast-enhanced pancreas CT scan obtained at arterial phase shows only moderate dilatation of main pancreatic duct (arrow) in tail of pancreas, and there is no evidence of obstructive mass. Atrophy with decreased enhancement of pancreatic tail is due to chronic pancreatitis.
B, C. T2-weighted (B) and gadolinium-enhanced (C) pancreas MR images show enhancing intraductal mass (short arrows) of main pancreatic duct in pancreatic body with dilatation of upstream main pancreatic duct (long arrow).
D. MR cholangiopancretography shows filling defect (short arrows) that is due to intraductal mass with dilatation of upstream main pancreatic duct (long arrow) and there is no dilatation of downstream main pancreatic duct.
E. Endoscopic retrograde pancreatogram shows filling defect (arrows) of contrast media that is due to mass in main pancreatic duct in pancreatic body.
F. Photograph of resected specimen shows mass (arrow) in dilated main pancreatic duct.