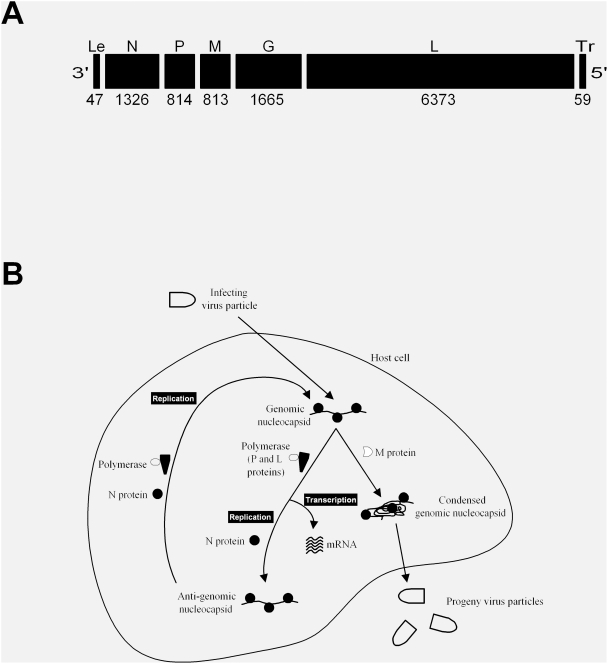
Figure 2. Overview of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV).
(A) Genome structure of VSV. Each gene is labeled by its single-letter abbreviation and length in nucleotides. The leader region (Le) encodes the genomic promoter, and the trailer region (Tr) encodes the complementary sequence to the anti-genomic promoter. (B) Growth cycle of VSV. The viral genomic RNA is used as a template for transcription of viral mRNA, which are translated to produce viral proteins. Accumulation of viral proteins enables amplification of the viral genome through an anti-genomic intermediate. Viral genomes are condensed, packaged and released as viral progeny into the extracellular environment.