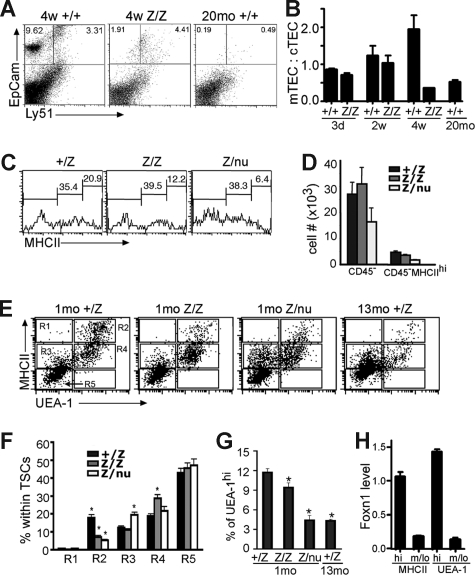
Figure 4.
Specific TEC subsets are more sensitive to the loss of Foxn1. (A) Gated CD45− stromal cells from 4-week thymi were stained for EpCam and Ly51 expression. The percentage of the Ly51−EpCam+ group was greatly reduced in lacZ/lacZ thymus compared to +/+. (B) Quantitative summary of mTEC:cTEC ratio at different stages. mTEC:cTEC ratio was reduced in lacZ/lacZ thymus at 4 weeks, similar to +/+ thymus at 20 months. (C) Gated CD45− TSCs from 5-week-old thymi analyzed for the MHCII expression. The percentage of MHCIIhi cells was greatly reduced in lacZ/lacZ and Z/nu thymi. (D) Quantitative summary of the total CD45− TSCs and MHC IIhi cell number. (E) Gated CD45− stromal cells from +/lacZ, lacZ/lacZ, and laccZ/nu thymi at 1 month and +/lacZ thymus at 13 months analyzed for MHCII and UEA-1 by flow cytometry. R1-R5 gates are indicated with boxes. (F) Summary of the percentages of cells in each gate for each genotype; significant changes relative to +/lacZ controls are indicated (*P < .05). (G) Summary of the percentage of UEA-1hi cells in 1-month thymus of each genotype and 13 months +/lacZ thymus (*P < .05). (H) MHCIIhi and UEA-1hi TEC subsets express higher levels of Foxn1. Quantitative real-time PCR was performed with cDNA from sorted TEC subsets from 4-week-old wild-type thymus (see Figure S4 for sorting gates). P < .001, n = 3.