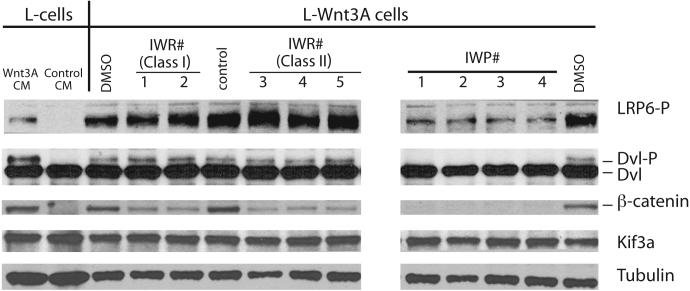
Figure 2. Biochemical evidence for Wnt/β-catenin pathway inhibition by IWR and IWP compounds.
L-Wnt-STF cells that exhibit constitutive Wnt pathway activation were incubated with IWR (10μM) and IWP (5μM) compounds for 24 hrs prior to lysis. Cellular lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis to determine levels of Lrp6 and Dvl2 phosphorylation, and β-catenin accumulation, all biochemical events associated with Wnt/β-catenin pathway activity. Predictably, IWPs blocked all three biochemical events whereas IWR compounds appear to block β-catenin accumulation without affecting Lrp6 and Dvl2 phosphorylation. Kif3A and tubulin serve as loading controls. Wild-type L-cells stimulated with exogenous Wnt3A protein provided in conditioned medium exhibit similar biochemical changes in Wnt pathway components as that observed in the L-Wnt-STF cells.