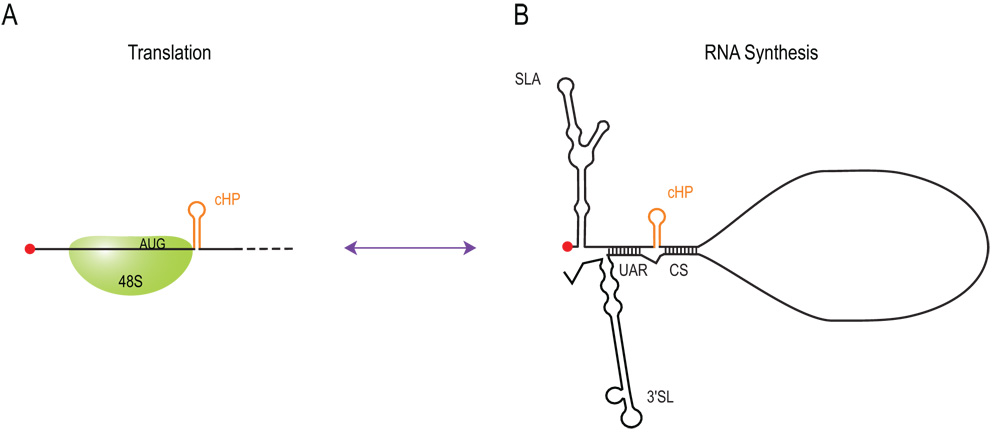
Figure 7. The cHP functions in translation and RNA synthesis of dengue virus.
(A) The cHP element functions in translation start site selection, probably by stalling the scanning 48S complex over the first AUG, enhancing its recognition as a start codon in the absence of a strong initiation context. The efficiency of first AUG selection is independent of the sequence of the cHP but is dependent on its position relative to the AUG and on its stability (Clyde and Harris, 2006). (B) Multiple structures at the 5' and 3' ends of flaviviruses have been shown to play an essential role in RNA synthesis (Alvarez et al., 2005; Filomatori et al., 2006a; Holden et al., 2006; Nomaguchi et al., 2003; Nomaguchi et al., 2004; Tilgner et al., 2005; You et al., 2001; You and Padmanabhan, 1999; Yu and Markoff, 2005; Zeng et al., 1998). The cHP element is also required for efficient RNA synthesis in a sequence-independent manner, possibly by forming part of the overall topology of the 5' end that initially binds the replicase complex or by stabilizing the cyclization interaction between the CS and UAR domains. Abbreviations: SLA, stem-loop A; UAR, upstream of AUG region; CS, cyclization sequence; 3'SL, 3' stem-loop.