Fig. 5.
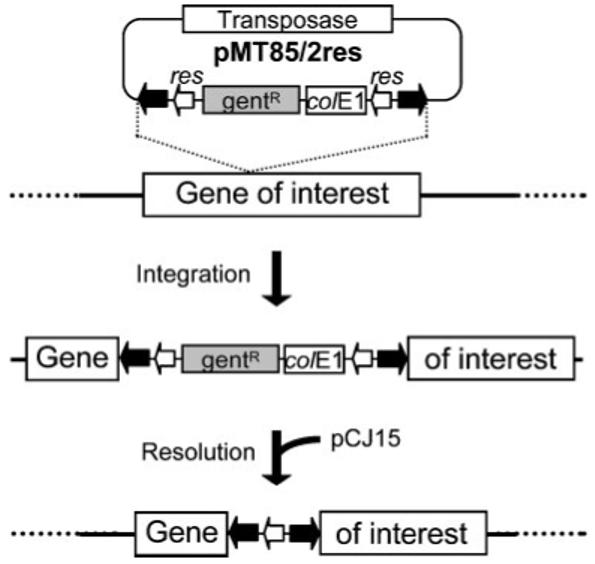
Schematic outline of the two-step procedure to obtain unmarked mutants. In the first step the transposon integrates into the chromosome. After selection of a mutant of interest, resolution of most of the transposed sequence is induced by the γδ resolvase that is encoded by a gene carried by the oriC plasmid pCJ15. Thick black arrows indicate the IRs of the transposon harboured by the plasposon pMT85/2res. Open arrows indicate the resolvase target sequences (res). colE1, replication origin in E. coli; gentR, gentamicin-resistance marker. The transposase-encoding gene is located outside the transposed region of the plasposon.
