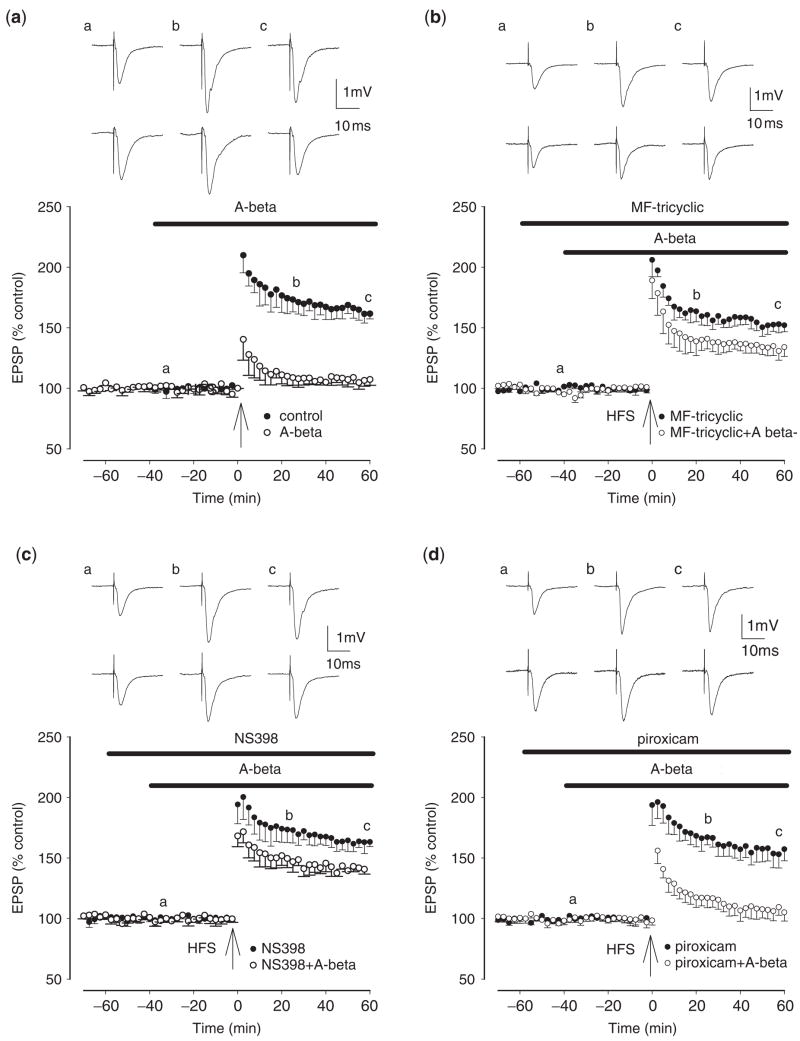
Fig. 2.
Selective COX-2, but not COX-1, inhibitors prevent the inhibition of LTP induction by synthetic, soluble Aβ42. (a) Control LTP induced by a single brief high-frequency stimulation (HFS) (closed circles) and LTP induction in the presence of synthetic, soluble Aβ42 (500 nM), applied 40 min prior to HFS (open circles). LTP in the presence of synthetic, soluble Aβ42 was significantly reduced from control. (b) The COX-2 inhibitor MF tricyclic (3 μM), applied 60 min prior to HFS, does not inhibit LTP induction (closed circles) but prevents the Aβ-mediated inhibition of LTP induction (open circles). (c) The COX-2 inhibitor NS-398 (20 μM), applied 60 min prior to HFS, does not inhibit LTP induction (closed circles) but prevents the Aβ-mediated inhibition of LTP induction (open circles). (d) The COX-1 inhibitor piroxicam (10 μM), applied 60 min prior to HFS, does not inhibit LTP induction (closed circles) and also does not prevent the Aβ-mediated inhibition of LTP induction (open circles). The traces a, b and c are field EPSPs at the times indicated by a, b and c on the graphs, with the top set of traces corresponding to the closed circles and the lower set of traces to the open circles.