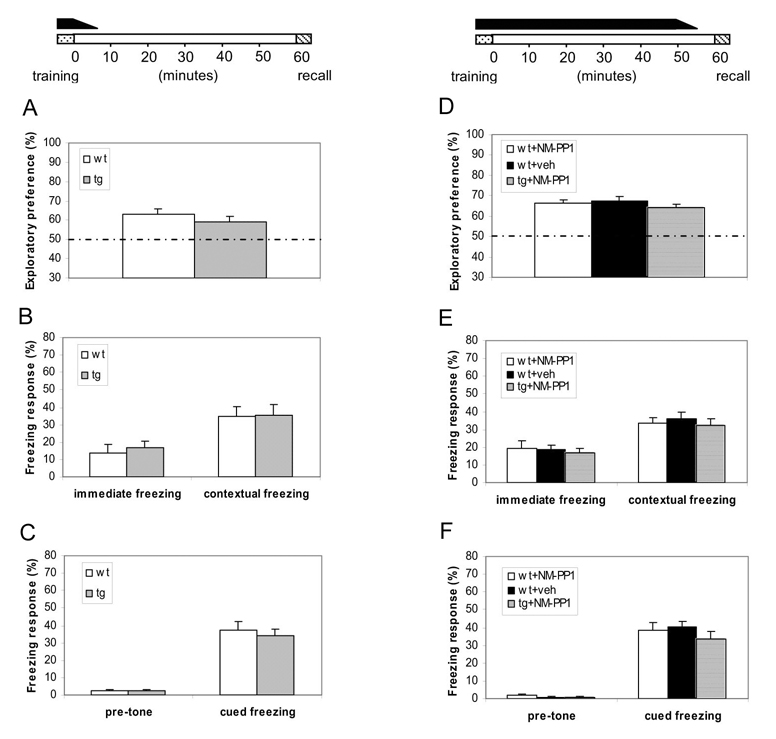
Figure 2. Normal short-term memory formation with elevated CaMKII.
(A–C) Under this “Learning-With-Elevated-CaMKII” paradigm, the temporally restricted presence of αCaMKII-F89G activity during learning did not impair memory acquisition and 1-hr retention as measured by three distinct memory tasks. The black bar on the top indicates the duration for the presence of αCaMKII-F89G activity. Animals were trained without any drug treatment. Immediately after training, they received the 1st i.p. injection of NM-PP1. The 2nd i.p. injection was administered 30 minutes later. The CaMKII activity of the transgenic mice during memory test were measured to be about 98.2 ± 3.8% of that of wild-type mice after receiving two NM-PP1 injections. (A) Indistinguishable performance in the novel object recognition test between Tg (n = 12) and wild-type mice (n = 12) (p > 0.05). (B) Indistinguishable performance in contextual conditioning between wild-type (n = 12) and transgenic mice (n = 12) (p > 0.05). (C) Cued conditioning in the same groups of mice. No significant difference was found between two groups (p > 0.05). All values are mean ± S.E.M. One-way ANOVA-Tukey was used for all the statistical analyses. (D–F) Under this “Learning/retention-With-Elevated-CaMKII” paradigm, transgenic mice with temporally restricted expression of αCaMKII-F89G activity during acquisition and post-training 55 minutes exhibited normal performance in the three tests. The black bar on the top indicates the duration for the presence of elevated αCaMKII activity. NM-PP1 was injected 10 minutes before recall. The CaMKII activity of the transgenic mice at the time of 1-hr-retention tests were estimated to be about 102.5 ± 6.3% of that of wild-type control mice under this injection protocol. (D) Normal performance in novel object recognition test in transgenic mice with NM-PP1 inhibition (n = 10, p > 0.05), compared with wild-type mice receiving vehicle (n = 10, p > 0.05) or wild-type mice with NM-PP1 inhibition (n = 11, p > 0.05). (E) Normal performance in contextual conditioning in transgenic mice with NM-PP1 (n = 10, p > 0.05), compared with wild-type mice with vehicle (n = 10, p > 0.05) or wild-type mice with NM-PP1 (n = 11, p > 0.05). (F) Normal performance in cued conditioning in transgenic mice with NM-PP1 treatment (n = 10, p > 0.05), compared with wild-type mice with vehicle (n = 10, p > 0.05) or wild-type mice with NM-PP1 inhibition (n = 11, p > 0.05). All values are mean ± S.E.M. One-way ANOVA-Tukey was used for all the statistical analyses.