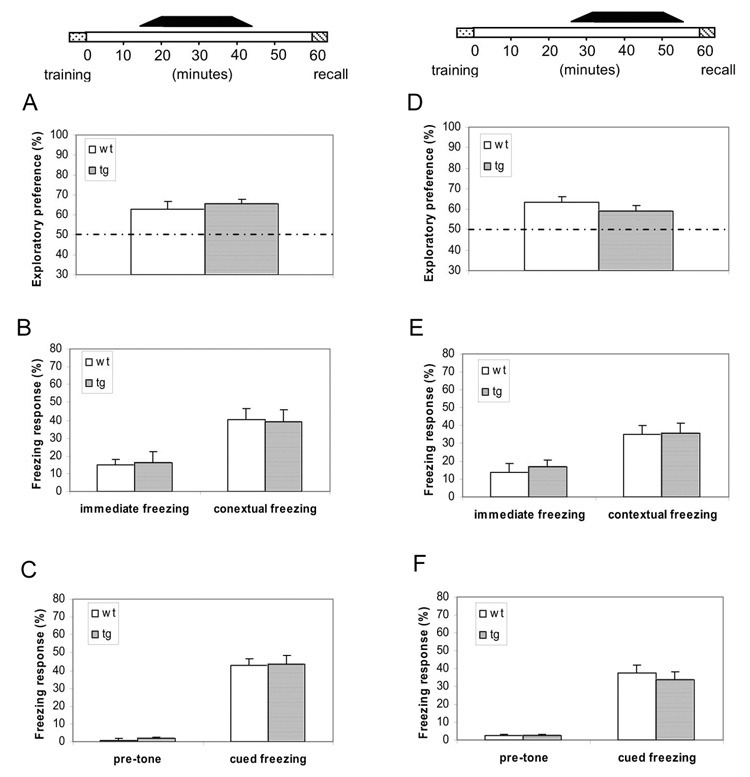
Figure 4. Unmasking of αCaMKII-F89G 15 minutes and beyond after learning did not disrupt the short-term memory.
(A–C) The black bar on the top indicates the duration for the presence of uninhibited CaMKII-F89G activity, 15 minutes after learning. Mice were given i.p. injection 15 minutes before novel object recognition training or 25 minutes before fear conditioning. The 2nd injection was given 25 minutes before retention tests. The CaMKII activity of the transgenic mice at the time of 1-hr-retention tests were estimated to be about 92.9 ± 5.9% of that of wild-type mice. (A) Normal novel object recognition memory in transgenic mice that unmasking αCaMKII-F89G activity took place 15 minutes after learning (12 animals each group, p > 0.05). (B) Normal contextual memory in both wild-type (n = 10), transgenic mice (n = 12). No significant differences were found in both immediate freezing and contextual conditioning between two groups (p > 0.05). (C) Normal cued fear memory in the same groups of mice. No significant differences were found (p > 0.05). All values are mean ± S.E.M. One-way ANOVA-Tukey was used for all the statistical analyses. (D–F) Unmasking of αCaMKII-F89G 30 minutes after learning did not disrupt the short-term memory. The black bar on the top indicates the duration for the presence of uninhibited αCaMKII-F89G. Mice were given NM-PP1 i.p. injection 5 minutes before object recognition training or 15 minutes before fear conditioning. The 2nd injection was given 10 minutes before retention test. The CaMKII activity of the transgenic mice at the time of 1-hr-retention tests were estimated to be about 95.4 ± 4.5% of that of wild-type mice. (D) Normal novel object recognition memory in transgenic mice after the late-stage (>25 minutes after training) unmasking αCaMKII-F89G activity (12 animals each group, p > 0.05). (E) Normal contextual memory in both wild-type (n = 10), transgenic mice (n = 12). No significant differences were found in both immediate freezing and contextual conditioning between two groups (p > 0.05). (F) Normal cued fear memory in the same groups of mice. No significant differences were found (p > 0.05). All values are mean ± S.E.M. One-way ANOVA-Tukey was used for all the statistical analyses.