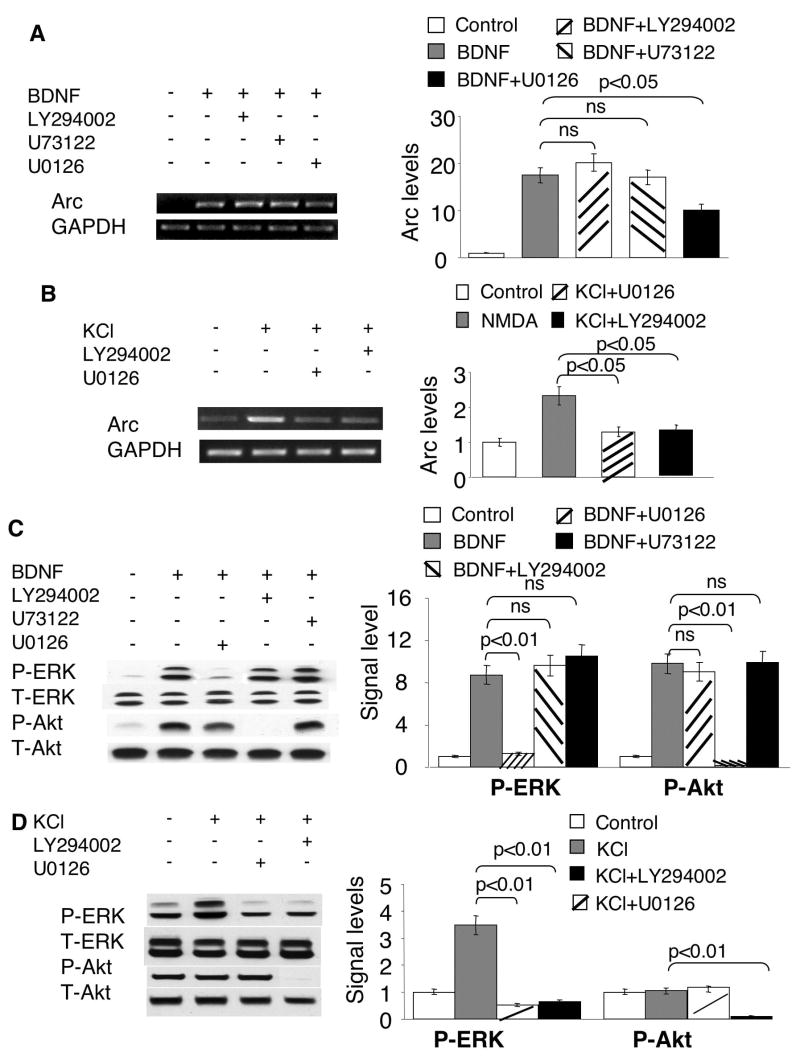
Fig. 2.
Regulation of Arc transcription by MAPK, PLC-γ and PI3K signaling. Cortical neurons were stimulated by 5ng/ml BDNF (A, C) or KCl (50mM) (B and D). Total RNA was extracted 1h after the treatments and used for semi-quantitative RT-PCR (A to B). Samples for Western blots (C, D) were collected 15min after the treatments. All inhibitors were applied 30min before BDNF and KCl stimulation. U73122 (5uM), LY294002 (30uM), and U0126 (10uM) were used to inhibit PLC-γ, PI3K and MEK, respectively. The levels of Arc and GAPDH mRNA were measured by RT-PCR using gene specific primers. Representative images are shown in the left panels, and quantification in the right panels. The relative intensity of Arc was normalized to GAPDH. C) The BDNF-induced ERK activation was inhibited by MEK inhibitor U0126, but not by PI3K inhibitor LY294002 or PLC-γ inhibitor U73122. The activation of ERK and PI3K was determined by the level of p-ERK and p-Akt, respectively. D) PI3K activity is required for the phosphorylation of ERK induced by membrane depolarization. Quantification of p-ERK and p-Akt was calculated from 3 independent experiments after normalization to T-ERK and T-Akt. Representative Western blot images are shown in the left panels, and quantification in the right panels.