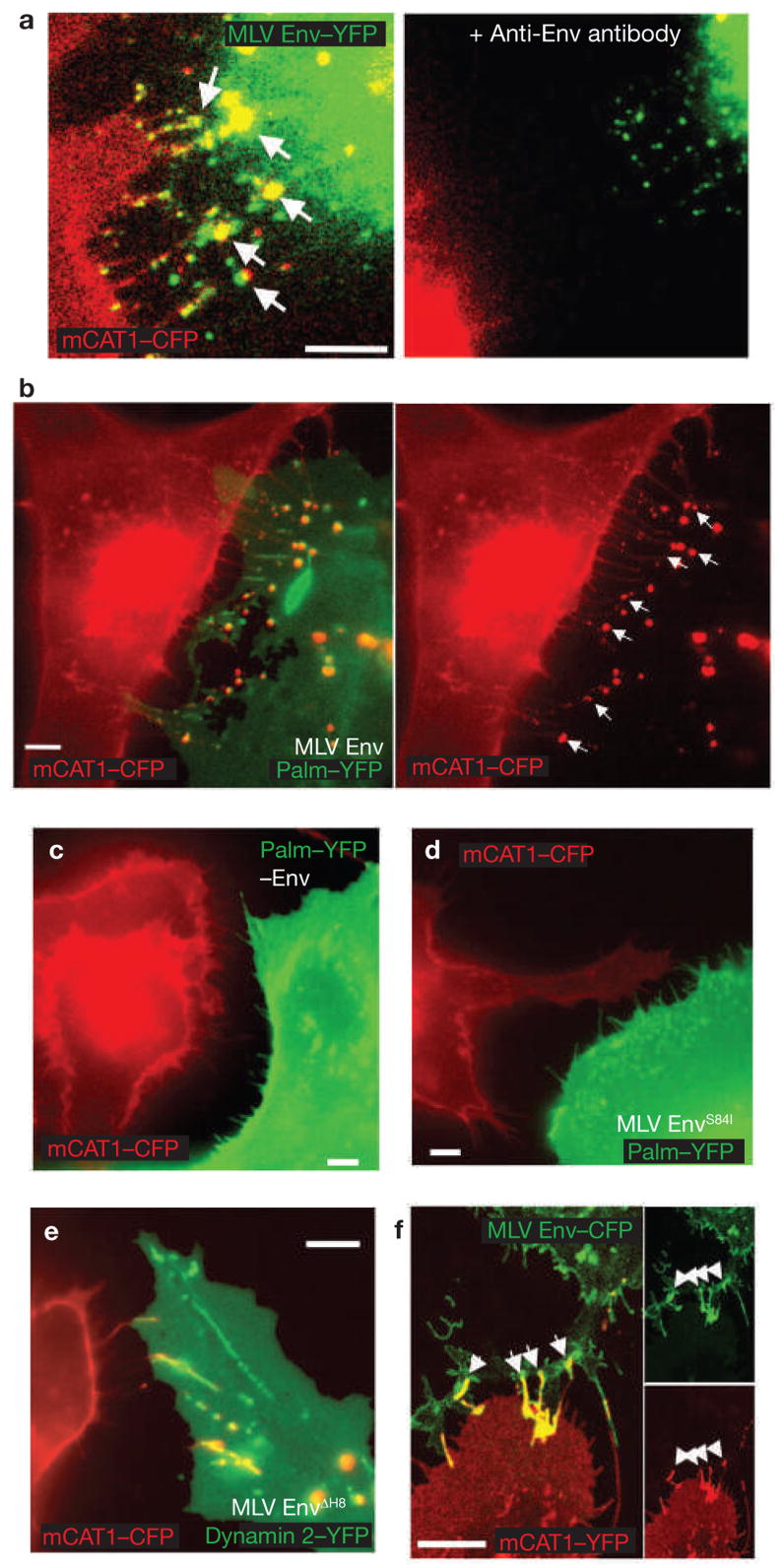
Figure 3.
Viral cytoneme formation depends on Env–receptor interactions. (a) An MLV infected Cos-1 cell expressing MLV Env–YFP (green) in coculture with an XC cell expressing mCAT1–YFP (red). The arrows indicate receptor–Env accumulation at filopodial contacts. The right panel shows the same area after 1 h treatment with neutralizing antibodies directed against the extracellular domain of MLV Env. (b) An MLV infected Cos-1 cell expressing unlabelled wild-type Env in coculture with an XC cell expressing mCAT1–CFP (red). To visualize the plasma membrane of virus producing cells, palmitylated YFP (palm–YFP, green) was coexpressed. Cytonemal contacts are indicated by white arrows. (c–e) Experiments as in b showing the behaviour of cell-cell contacts in the absence of Env expression (c), the expression of a mutant Env impaired in receptor-binding (S84I, d) or the expression of a mutant Env (ΔH8, e) capable of receptor-binding, but impaired in a post-binding step. In e, infected cells were identified by coexpression of the endocytic marker dynamin 2–YFP. (f) HEK 293 cells expressing MLV Env–CFP (green) in coculture with an XC cell expressing receptor mCAT1–YFP (red). Arrows indicated sites of Env–receptor accumulation. Panels on the right show unmerged images. The scale bars represent 5 μm in a–f.