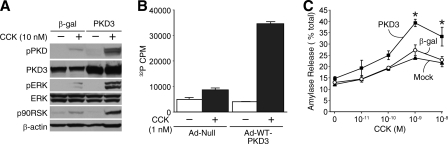
FIGURE 6.
Overexpression of PKD3 potentiates MEK/ERK/RSK signaling and promotes CCK-induced amylase release. A, isolated mouse acini were infected with control adenovirus expressing β-galactosidase (β-gal) or adenovirus expressing wild-type PKD3 (PKD3) for 15 h. Acini were then treated with vehicle or CCK (10 nm) for 30 min; protein was extracted and analyzed by Western blotting. B, acini were infected with control null-adenovirus (Ad-Null) or Ad-WT-PKD3 for 24 h. Acini were then treated with vehicle or CCK (10 nm) for 30 min. Cellular proteins were immunoprecipitated using the PKD3-specific antibody and then analyzed by in vitro kinase assay. Results represent the means ± S.E. for three separate kinase assays. C, acini were subjected to mock infection or infection with 108 infectious units/ml adenovirus expressing β-galactosidase (β-gal) or WT-PKD3 for 15 h. Acini were then treated with increasing concentrations of CCK for 30 min. The media supernatant from each sample was collected and analyzed for amylase activity. Results represent the means ± S.E. for four independent experiments. Three pairwise comparisons were carried out for mock versus β-galactosidase versus WT-PKD3 comparisons for each CCK concentration; the asterisk indicates that the mean of WT-PKD3 is significantly greater than β-gal and mock infection (p < 0.05) at each CCK concentration.