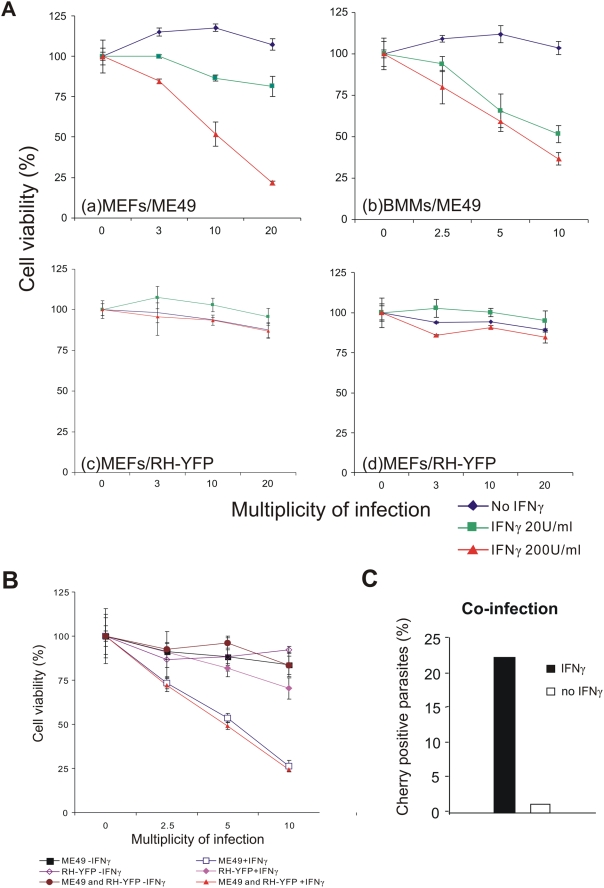
Figure 7. Virulent T. gondii are resistant to the IRG- and IFNγ-dependent cell-necrotic programme.
(A) MEFs (a, c–d) or BMMs (b) were seeded into 96 well plates and induced with the indicated dose of IFNγ for 24 hours. Cells were then infected with T. gondii avirulent strain ME49 (a–b) or virulent strain RH-YFP (c–d) for 8 hours at the indicated MOIs. Cell viabilities were measured and expressed as percentages of those recorded for uninfected cells (MOI = 0). (B) MEFs were treated as described in (A) and infected for 8 hr with ME49 or RH-YFP alone or co-infected with ME49 and RH-YFP simultaneously. Cell viabilities were measured and expressed as percentages of those recorded for uninfected cells. (C) MEFs were transfected with pCherry and induced with 200 U/ml IFNγ for 24 hours (black bar) or left untreated (white bar). Cells were then co-infected with ME49 and RH-YFP T. gondii strains (MOI 5 for each strain) for 4 hours. Permeabilised parasites containing Cherry were counted, in cells containing at least one RH-YFP parasite, as a proportion of all intracellular ME49. 200–300 PVs per data point were counted blind.