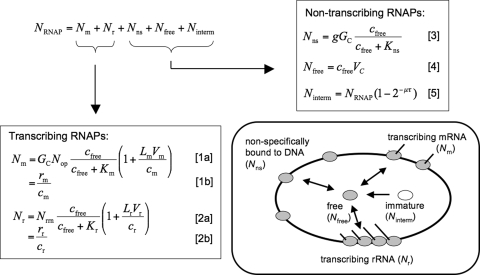
Fig. 1.
Model for the partitioning of RNAPs. In exponentially growing cells all RNAPs are taken to fall into 5 classes, RNAPs transcribing mRNA (Nm) and rRNA (Nr), RNAPs nonspecifically bound to DNA (Nns), free RNAPs (Nfree), and RNAP assembly intermediates (immature RNAPs, Ninterm). The total number of RNAPs per cell (NRNAP) is the sum of the number of RNAPs in these classes. Our model describes the numbers of RNAPs in each class by equations that link them to measured biophysical parameters of the cell (see SI Text for a detailed description and Tables S1 and S2 for the parameter values, many of which are growth-rate dependent). The numbers of transcribing RNAPs (Nr and Nm) are both described by a microscopic model Eqs. 1a, 2a, and estimated directly from measured RNA synthesis rates Eqs. 1b and 2b.