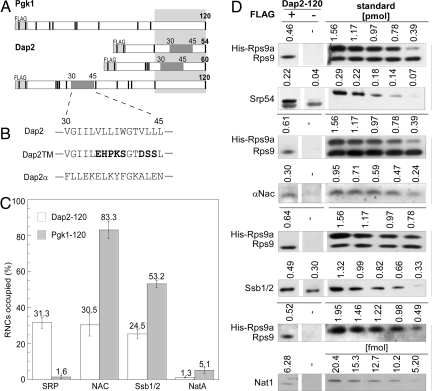
Fig. 1.
The exposed SA of Dap2 attracts SRP and disfavors binding of other ribosome-associated protein biogenesis factors to RNCs. (A) Schematic representation of nascent Pgk1 of 120 aa, and Dap2 of 54, 60, and 120 aa. The type II membrane protein Dap2 contains a SA localized between amino acids 30 and 45. The SA is indicated in dark gray; the portion of the nascent chains covered by the ribosomal tunnel is indicated in light gray. Nascent chains contained an N-terminal FLAG tag that was used for the purification of RNCs. The positions of lysines, important for chemical cross-linking, are marked as black bars. (B) SA of Dap2 and of the mutant versions, Dap2TM, and Dap2α. (C) Occupation of Dap2-120 or Pgk1–120 RNCs with RPBs in percent of RNCs. Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean (SEM). (D) Immunoblots for the quantification of Srp54, αNAC, Ssb1/2, and Nat1 on Dap2-120 RNCs exemplifies the data in C. RNCs carrying FLAG-tagged nascent Dap2 were isolated by native immunoprecipitation using αFLAG-coated beads. Aliquots of the material recovered and purified standard proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting. Signals obtained from the same exposure of a single gel are boxed. In case of the standard, numbers above the lanes give the amount of the respective purified protein loaded to the gel in picomoles or femtomoles, respectively. The standard protein His-Rps9a was supplemented with total yeast extract to ensure quantitative recovery during the procedure. Standard curves (Fig. S2) were used to determine the amount of RNCs and attached factors pulled down via the FLAG-tagged nascent chains. The background derived from an identically treated sample containing RNCs carrying the same, but nontagged, nascent chain was subtracted. The amount of His-Rps9a in the samples was divided by the factor 0.7 corresponding to Rps9a/b deviation from the mean value of ribosomal proteins previously determined (ref. 22 and Fig. S2).