Fig. 5.
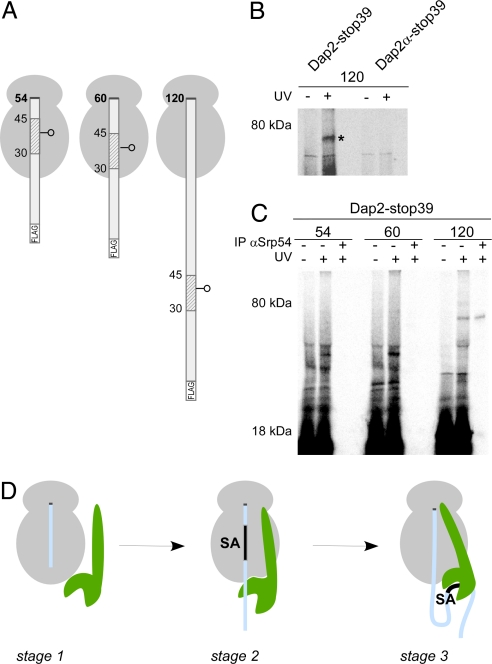
A Dap2 SA inside the ribosomal tunnel is not adjacent to SRP. (A) RNCs with 54-, 60-, and 120-residue Dap2 nascent chains with a single photo probe in the middle of the SA sequence are depicted. (B) 35S-methionine-labeled RNCs with εANB-Lys probes at position 39 of 120-residue length FLAG-Dap2 or FLAG-Dap2α were photolyzed (+UV). As a control, a parallel sample was not illuminated with UV light (−UV). RNCs were then isolated via the FLAG tag and analyzed by autoradiography. The cross-link between Dap2-120 and Srp54 is labeled with an asterisk. (C) 35S-methionine-labeled RNCs with εANB-Lys probes at position 39 of nascent FLAG-Dap2 were photolyzed (+UV) or kept in the dark (−UV) and were then isolated via the FLAG tag. A sample corresponding to 2 times the amount of the material shown in the +UV lane was subjected to immunoprecipitation under denaturing conditions using αSrp54 coupled to protein A Sepharose beads (IP αSrp54). (D) Three-stage model of SRP binding to RNCs. Stage 1: SRP (green) binds weakly to translating ribosomes (gray). This mode of interaction is independent of the length and type of nascent chain (light blue), but SRP affinity is higher than to nontranslating ribosomes. Stage 2: Upon synthesis of a SA, the interaction with the ribosome is strengthened and SRP localizes close to the exposed portion of the nascent polypeptide. The interaction is salt sensitive, suggesting that it is mainly electrostatic in nature. Stage 3: When the SA emerges from the tunnel, SRP binds to it with high affinity. The interaction is now salt resistant, thereby suggesting that hydrophobic interactions contribute significantly. In this stage, translation is arrested and the RNC–SRP complex is targeted to SRP receptor in the ER membrane. For details and references, see Discussion.