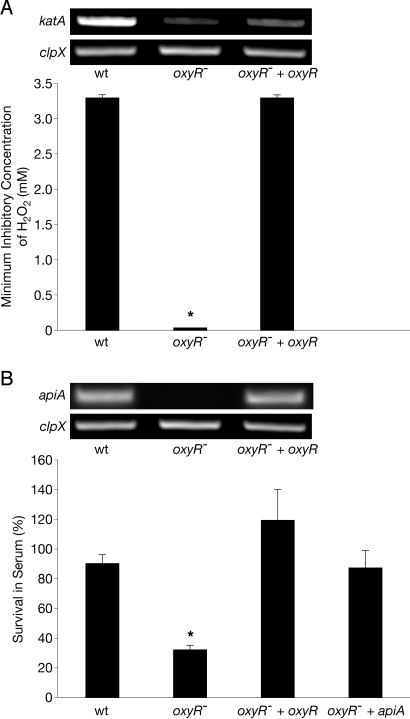
Fig. 4.
The A. actinomycetemcomitans oxyR− mutant is hypersusceptible to killing by H2O2 and human serum. (A) The H2O2 minimum inhibitory concentration (lowest concentration necessary to inhibit visible growth of an organism) of WT A. actinomycetemcomitans (wt), the A. actinomycetemcomitans oxyR− mutant (oxyR−), and the genetically complemented A. actinomycetemcomitans oxyR− mutant (oxyR− + oxyR). (Inset) RT-PCR analysis of mRNA levels of katA and the clpX constitutively expressed control in the wt oxyR−, and oxyR− + oxyR after H2O2 exposure. (B) Survival of wt, oxyR−, oxyR− + oxyR, and oxyR− constitutively expressing apiA (oxyR− + apiA) in the presence of 50% (vol/vol) normal human serum. Percent survival was calculated as follows: number of cells recovered from normal human serum treatment/number of cells recovered from heat-inactivated serum treatment. (Inset) RT-PCR analysis of mRNA levels of apiA and the clpX constitutively expressed control in the wt, oxyR−, and oxyR− + oxyR after H2O2 exposure. As a control, exogenous catalase was added to serum to ensure that any phenotype observed was not attributable to endogenous H2O2 within serum. Error bars represent SEM. *P < 0.004 via Student's t test, n = 3.