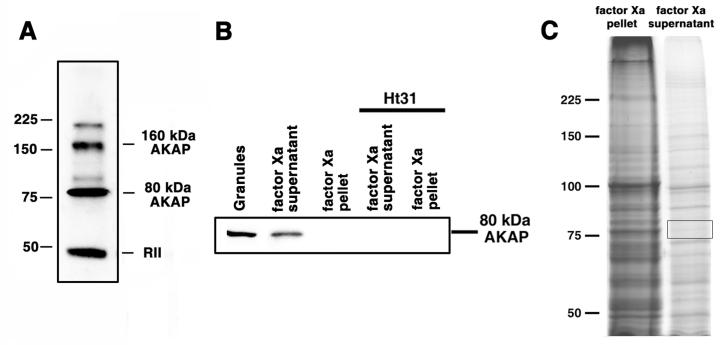
Figure 1. 80 kDa AKAP is released in solution after treatment of pigment granule preparations with the highly selective protease factor Xa.
A, blot overlays of pigment granule preparations with recombinant RIIα; RIIα binds two polypeptides in the pigment granule preparations with approximate molecular masses of 80 kDa and 160 kDa, as well as to itself. B, blot overlays of the indicated samples with recombinant RIIα in the absence (left three lanes) or presence (right two lanes) of Ht31. Treatment of pigment granules with factor Xa releases the 80 kDa RIIα-binding protein into solution. C, Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE gels of a pellet (left) and a supernatant (right) obtained by centrifugation of a pigment granule preparation treated with factor Xa; most of the pigment granule proteins remained bound to pigment granules after the protease treatment; boxed region on the right lane shows the gel area used for the mass-spectrometry analysis.