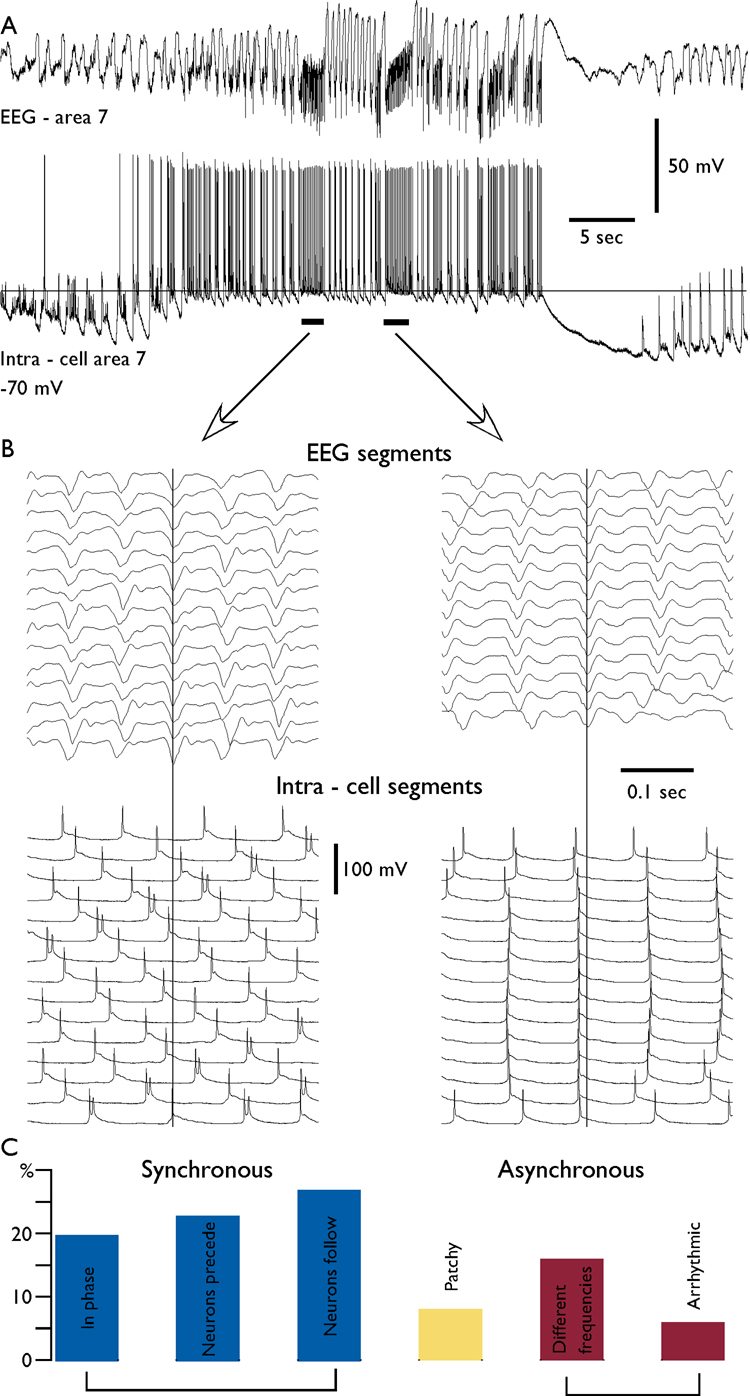
Fig. 4. Variability in neuron – field synchronization during fast runs.
A. Depth-EEG and simultaneous intracellular recordings during an electrographic seizure. The distance between field potential electrode and intracellularly recorded neuron was 2 mm. B. A superposition of field potential (upper panels) and intracellular recordings (lower panels) during fast runs for the two consecutive periods of fast runs. Note the different frequencies of oscillations in the EEG and intracellularly recorded neuron during the first period and in phase synchronization during the second period. C. the distribution of patterns of synchronization for 312 periods of fast runs. The coherent patterns (0 time lag or with phase shift) constituted 70 % of cases. Arrhythmic stands for periods of fast runs recorded at one electrode, while the activity in another electrode was not rhythmic.