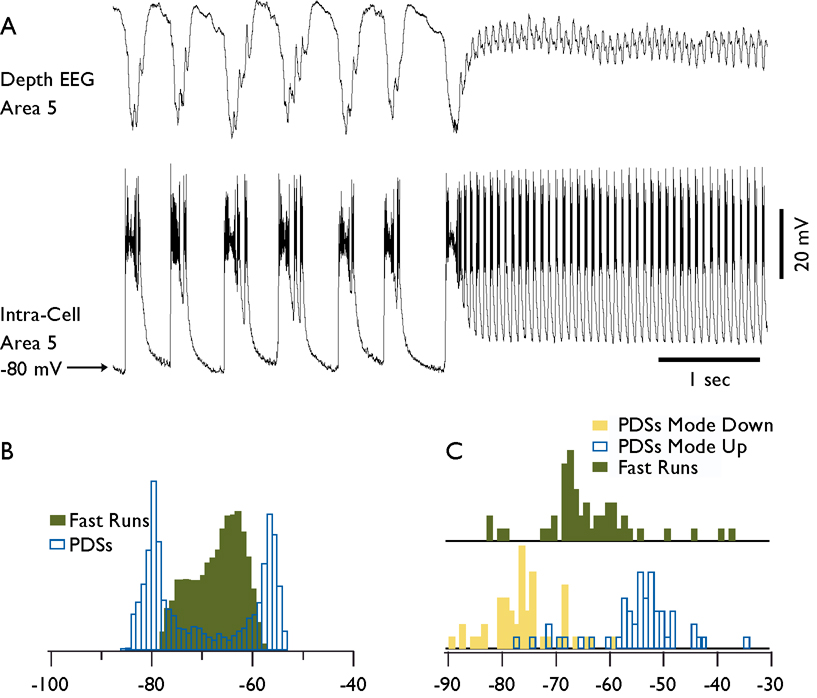
Fig. 7. Membrane potential of cortical neurons during spike-wave and fast run components of seizures.
A. Field potential and intracellular recordings during a fragment of electrographic seizure containing spike-wave complexes and a fast run period. B. Histogram of membrane potential during spike-waves (transparent bars) and fast run (green bars) from the neuron shown in A. Note the presence of two peaks during spike-wave complexes and one peak during fast runs. PDS stands for paroxysmal depolarizing shift. C. Distribution of membrane potential for hyperpolarized mode of spike-wave discharges (yellow bars), for depolarized mode of spike-wave discharges (transparent bars), and for fast runs (green bars). Bins are 1 mV for histograms in B and C.