Fig. 1.
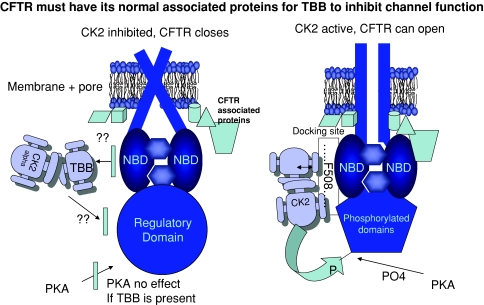
CK2 inhibition only closes cell attached CFTR. CK2 docks with CFTR using part of a sequence KENIIFGVSYDE on the periphery of the nucleotide binding domain 1 (NBD) that contains F508 whose deletion causes most CF disease. In the presence of identical concentrations of TBB, a CK2 inhibitor, only the cell attached CFTR shows rapid channel closure (less than 80 s) as depicted in the cartoon. If TBB is present PKA cannot open CFTR. Once a patch of membrane is pulled away from the cell (not shown), TBB is without inhibitory effect suggesting the CFTR environment is important for the CK2 inhibition. The details can be found in Pagano et al. [16]