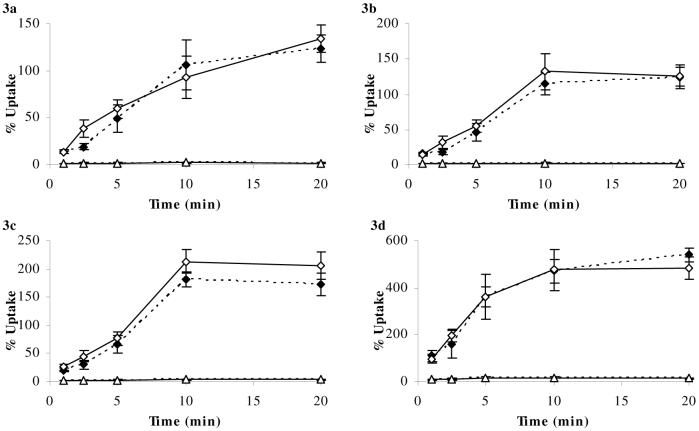
Figure 3a-d. Percentage Uptake of [3H]corticosterone and [14C]sucrose in abcb1a/b (+/+) and abcb1a/b (-/-) mice using in-situ brain perfusion.
[3H]corticosterone (3.8 nM) along with [14C]sucrose (vascular space marker; 0.5-1.0 nM), was administered by a slow-drive syringe pump into the artificial plasma. Following the desired isotope perfusion time period up to 20 minutes, the mouse was decapitated, and selected areas of the brain were dissected. The concentration of [3H] or [14C] radioactivity in the brain tissue (dpm g-1) is expressed as a percentage of that in artificial plasma (dpm ml-1). The uptake of [3H]corticosterone (n=28-51/strain) in abcb1a/b (-/-) mice was not significantly different compared to abcb1a/b (+/+) mice in the frontal cortex (Fig. 3a), hippocampus (Fig. 3b), hypothalamus (Fig. 3c), or pituitary gland (Fig. 3d). [14C]Sucrose uptake was not influenced by the mouse strain.
♦ (dotted line) [3H]cortiscosterone (abcb1a/b (+/+) mice); ◊ (solid line) [3H]corticosterone (abcb1a/b (-/-) mice); ▲ (dotted line) [14C]sucrose (abcb1a/b (+/+) mice); ∆ (solid line) [14C]sucrose (abcb1a/b (-/-) mice)