Fig 2.
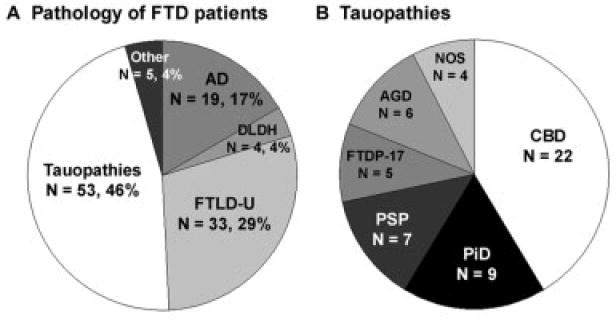
Neuropathology of frontotemporal dementia (FTD). (A) Primary neuropathological diagnosis of patients who presented clinically with frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD). The number of patients and percentage of total are indicated. The “other” category includes patients with Lewy body disease (n = 2), Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (n = 1), cerebrovascular disease (n = 1), and normal adult brain (n = 1). Additional, less robust pathology was present in 20.4% of patients and consisted of either a second, less robust, neurodegenerative disorder present in 13.8% of patients or cerebrovascular disease present in 6.6% of patients. (B) Neuropathological subtypes of tauopathies. The number of patients in each category is indicated. AD = Alzheimer’ disease; AGD = argyrophilic grain disease; CBD = corticobasal degeneration; DLDH = dementia lacking distinctive histopathology; FTDP-17 = frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17; FTLD-U = frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin-positive inclusions; NOS = not otherwise specified; PiD = Pick’s disease; PSP = progressive supranuclear palsy.
