Fig. 2.
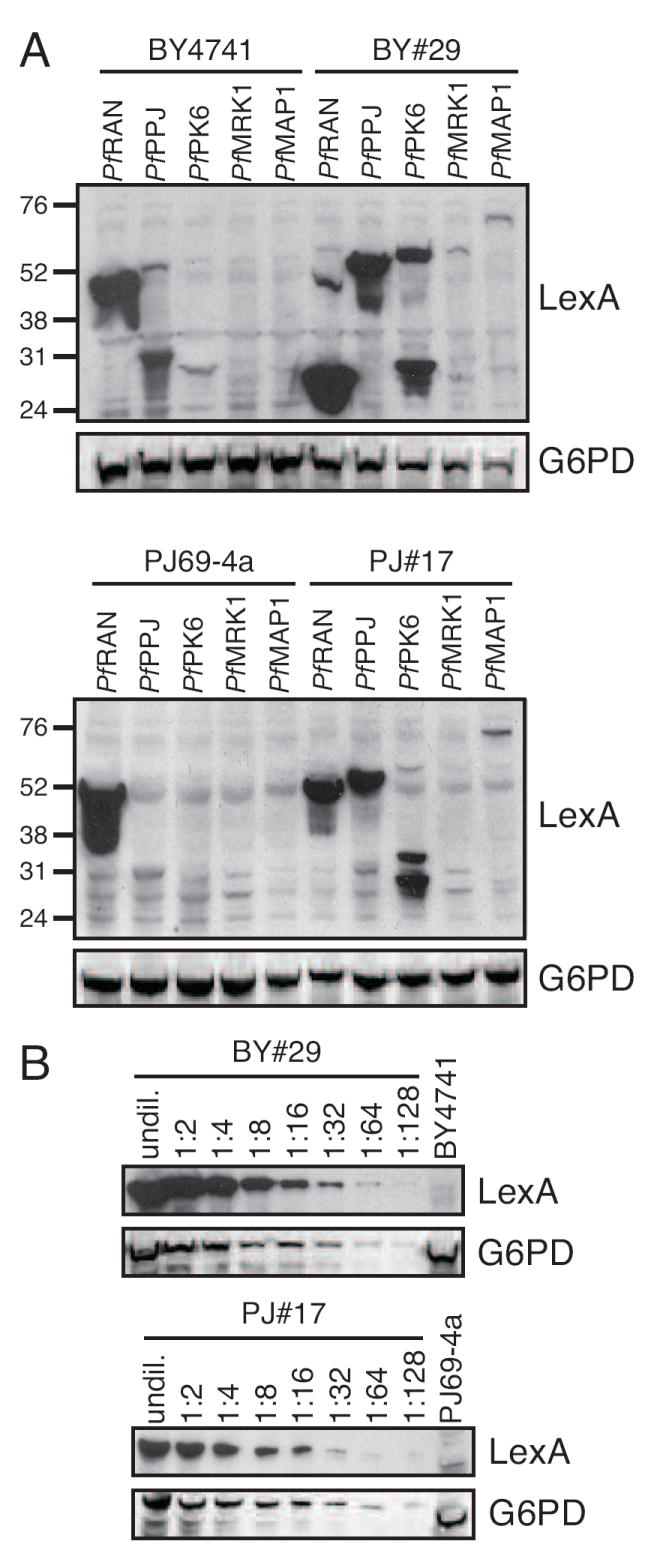
A. Expression of P. falciparum proteins in mutant yeast strains that express PfOMPDC. Total protein lysates were prepared from the parental yeast strains BY4741 and PJ69-4a, and from PfOMPDC-expressing strains BY#29 and PJ#17, transformed with the lexA expression plasmid or plasmids encoding the P. falciparum genes PfRAN, PfPPJ, PfPK6, PfMRK1, and PfMAP1 as fusions with the lexA gene. Lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE and subjected to immunoblot analysis with an anti-LexA antibody. The blots were then reprobed with an antibody against the yeast glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase as a loading control. Molecular weight markers are indicated at left. The predicted sizes of the LexA-PfRan, LexA-PfPK6, LexA-PfPPJ, LexA-PfMRK1, and LexA-PfMap1 fusion proteins are 46, 58, 59, 59, and 114 kDa, respectively. B. Estimate of the fold increase in LexA-PfPPJ expression in BY#29 and PJ#17 compared to parental strains. Undiluted and two-fold serial dilutions of total protein lysates from BY#29 and PJ#17 and undiluted total lysate from BY4741 and PJ69-4a expressing PfPPJ were subjected to SDS-PAGE and probed with anti-LexA antibody. Blots were reprobed with an antibody against the yeast glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) as a loading control.
