Abstract
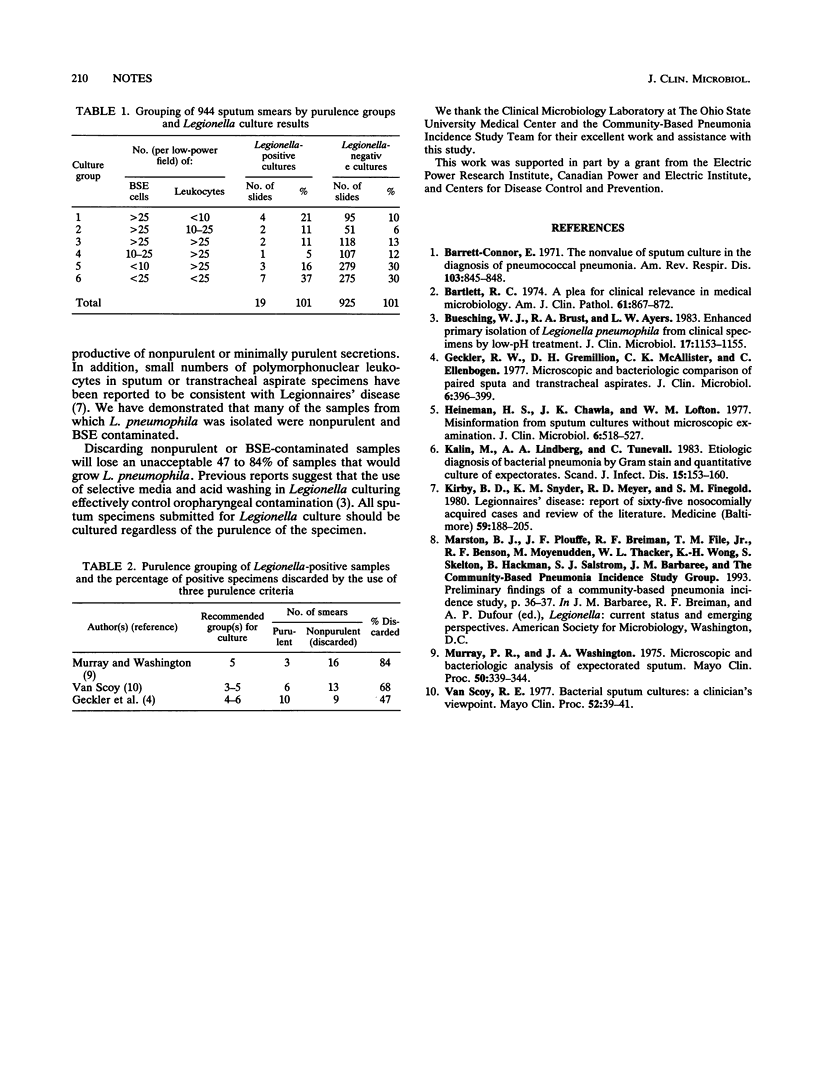
Previous studies have shown the benefit of sputum purulence screens in routine bacterial culture. We have correlated 944 sputum smear and Legionella pneumophila culture results and demonstrated that 47 to 84% of L. pneumophila-positive samples would have been discarded by using established sputum purulence screens. We recommend acceptance of all specimens submitted for Legionella culture.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett-Connor E. The nonvalue of sputum culture in the diagnosis of pneumococcal pneumonia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Jun;103(6):845–848. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.103.6.845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett R. C. A plea for clinical relevance in medical microbiology. Am J Clin Pathol. 1974 Jun;61(6):867–872. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/61.6.867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buesching W. J., Brust R. A., Ayers L. W. Enhanced primary isolation of Legionella pneumophila from clinical specimens by low-pH treatment. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;17(6):1153–1155. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.6.1153-1155.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geckler R. W., Gremillion D. H., McAllister C. K., Ellenbogen C. Microscopic and bacteriological comparison of paired sputa and transtracheal aspirates. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Oct;6(4):396–399. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.4.396-399.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heineman H. S., Chawla J. K., Lopton W. M. Misinformation from sputum cultures without microscopic examination. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Nov;6(5):518–527. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.5.518-527.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalin M., Lindberg A. A., Tunevall G. Etiological diagnosis of bacterial pneumonia by gram stain and quantitative culture of expectorates. Leukocytes or alveolar macrophages as indicators of sample representativity. Scand J Infect Dis. 1983;15(2):153–160. doi: 10.3109/inf.1983.15.issue-2.05. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby B. D., Snyder K. M., Meyer R. D., Finegold S. M. Legionnaires' disease: report of sixty-five nosocomially acquired cases of review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1980 May;59(3):188–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. R., Washington J. A. Microscopic and baceriologic analysis of expectorated sputum. Mayo Clin Proc. 1975 Jun;50(6):339–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Scoy R. E. Bacterial sputum cultures. A clinician's viewpoint. Mayo Clin Proc. 1977 Jan;52(1):39–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


