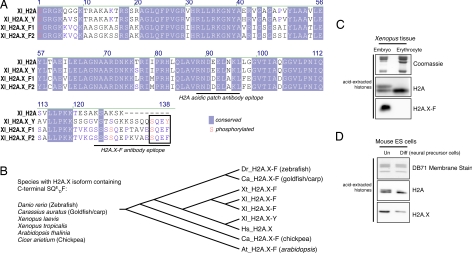
Fig. 1.
Protein sequence of H2A.X isoforms and H2A.X enrichment in embryonic cells. (A) Multiple sequence alignment of Xenopus H2A, H2A.X-Y, and H2A.X-F1 and F2 proteins as determined by ClustalW. Conserved amino acids are shaded in blue, and amino acids known to be phosphorylated are written in red. The epitopes of the H2A “acidic patch” and the H2A.X-F antibodies are underlined. (B) Species containing an H2A.X with a C-terminal SQxF motif are listed, as is a phylogenetic tree (determined by sequence parsimony). (C) Coomassie-stained and H2A- and H2A.X-F-specific immunoblots of histones from Xenopus early-embryo equivalent pronuclei and erythrocytes. (D) H2A- and H2A.X-specific immunoblots of isolated histones from undifferentiated and differentiated mouse ES cells.