Figure 1.
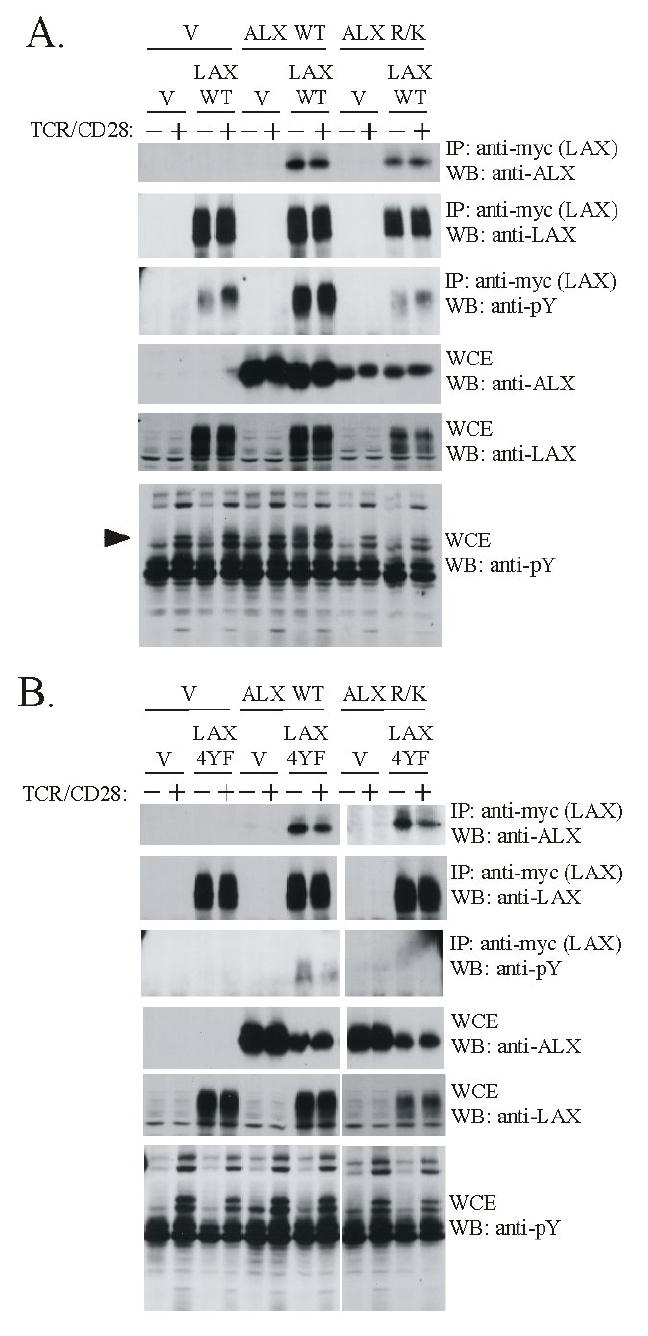
The association of ALX with LAX occurs independently of phosphotyrosine recognition. Jurkat cells were co-transfected with expression plasmids for either wild type ALX or an ALX SH2 domain mutant incapable of phosphotyrosine binding (ALX R/K) along with either (A) wild type LAX or (B) a LAX mutant (LAX 4YF) in which the four sites of tyrosine phosphorylation were replaced. Empty vector (V) was used to standardize total plasmid transfected between samples. The cells were left unstimulated (-) or stimulated for 2 min. (+) with antibodies to TCR and CD28. Whole cell extracts were made (WCE) and subject to immunoprecipitation (IP) with antibodies to a myc-epitope present on LAX. Western blotting (WB) was then performed with the indicated antibodies to analyze expression of LAX and ALX in the WCEs and IPs. Note that LAX appears as a “smear” on immunoblots, which is likely an effect of glycosylation, as is often found in transmembrane proteins. The minor, lower molecular weight bands observed in LAX immunoblots are likely incompletely modified forms of the protein. Anti-phosphotyrosine blotting with 4G10 confirmed TCR/CD28 stimulation, as well as LAX phosphorylation. The arrowhead indicates the position of a tyrosine phosphorylated band present in unstimulated cells only upon transfection with both WT ALX and LAX. This band is likely LAX, based on molecular weight, and consistent with the substantial increase in phosphorylated LAX in the immunoprecipitates observed upon cotransfection with ALX.
