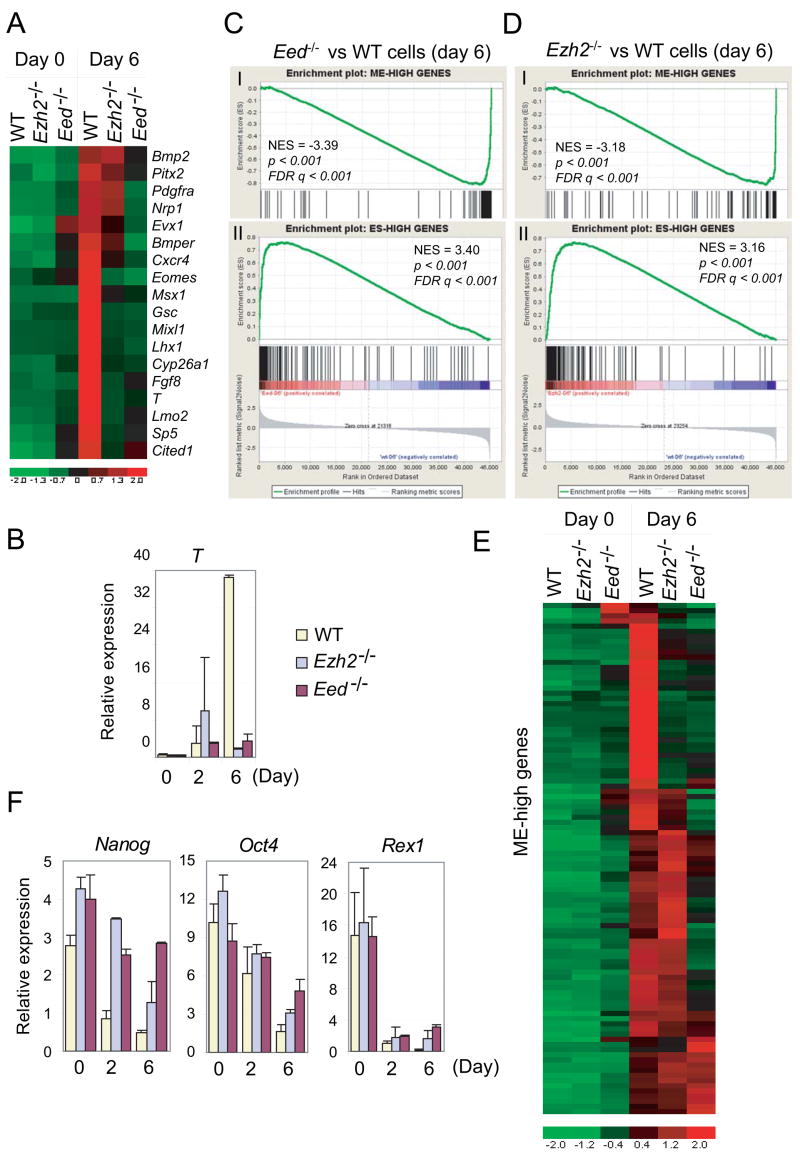
Figure 6. Ezh2 and Eed are required for mesoendodermal (ME) differentiation.
(A) Heat map showing impaired activation of known mesodermal markers in Ezh2−/− and Eed−/−cells as compared to wild-type (WT) cells.
(B) RT-qPCR analysis of T expression along ES cell differentiation by LIF withdrawal.
(C–D) GSEA profiles of ME-high (panel I) and ES-high (panel II) genes by comparing day-6 differentiated Eed−/− (C) or Ezh2−/− (D) cells to wild-type cells.
(E) Heat map of ME-high genes in wild-type and mutant ES cells.
(F) RT-qPCR analysis of pluripotency markers along ES cell differentiation.