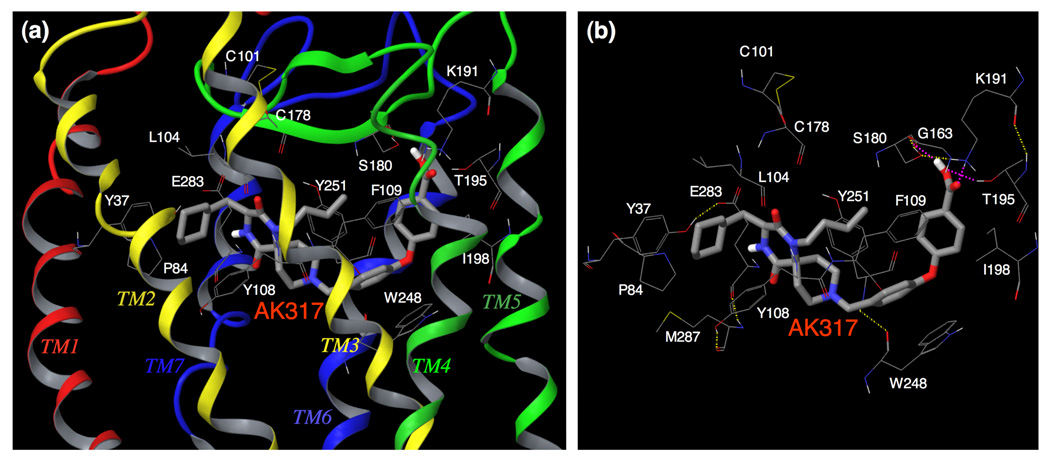
Fig. 6. Amino acid residues forming the binding cavity within CCR5 for AK317.
(a) The binding mode of AK317 within CCR5 is shown. (b) The intramolecular hydrogen bond interactions of CCR5 defining the binding cavity, and the binding interactions of AK317 with CCR5 are shown. AK317 has hydrogen bond interactions with S180, K191, and T195 (shown in pink dotted line). Other residues in the binding cavity are predicted to have hydrophobic interactions with AK317. As in the case of AK530, there are several intra-molecular hydrogen bond networks (shown in yellow dotted line) that define the shape of the CCR5 binding cavity for AK317. There is a network involving, S180 (ECL2), G163 (TM4), K191 (TM5), and T195 (TM5), and another involving Y37 (TM1), E283 (TM7), M287 (TM7), and Y108 (TM3). The conformation involving amino acid residues in the latter network differs from that of the case of AK530 binding. It appears that CCR5 undergoes different conformational changes to accommodate different inhibitors.