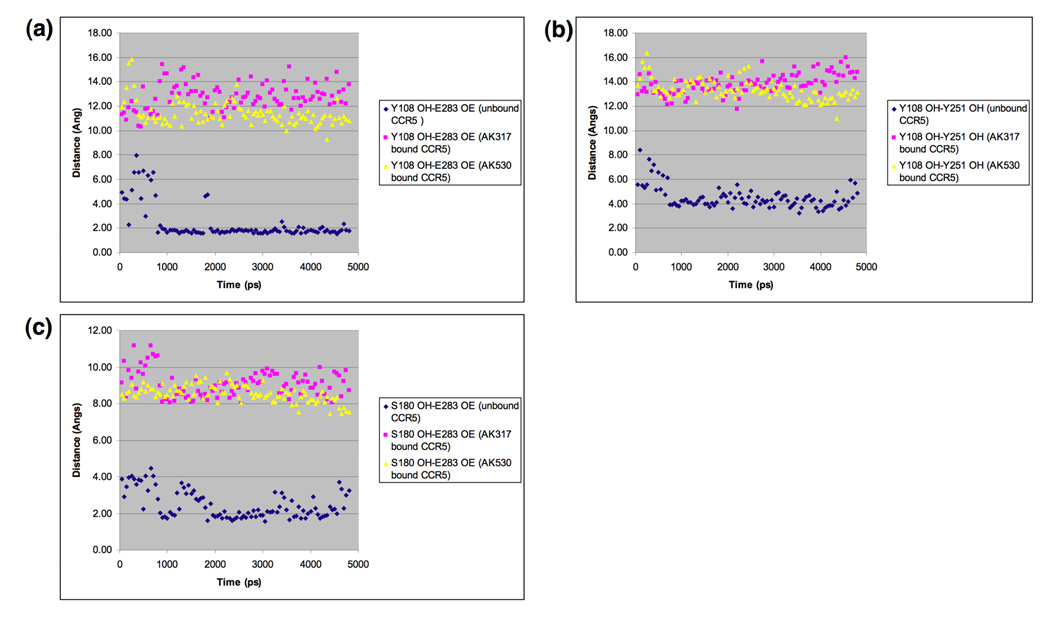
Fig. 7.
Key interatomic distances from molecular dynamics simulation of AK317-bound, AK530-bound, and inhibitor-unbound CCR5. Molecular dynamics simulation for 4800 ps for AK317- and AK530-bound CCR5 was conducted and critical interatomic distances between key amino acids were determined. A hydrogen bond is present if the interatomic distance is less than 3Å. (a) Distance between Y108 (hydroxyl hydrogen, PDB atom type OH) and E283 (carboxylate oxygen, PDB atom type OE). In the inhibitor-unbound conformation, there is a strong hydrogen bond interaction between Y108 in TM3 and E283 in TM7. Y108 and E283 have to move away from each other to form the binding cavity for the inhibitor to bind, and there is no hydrogen bond between these residues after AK317 and AK530 bind. (b) Distance between Y108 and Y251 hydroxyl oxygen): The tyrosines have moved away from each other after inhibitor binding. (c) Distance between E283 (carboxylate oxygen, PDB atom type OE) and S180 (hydroxyl hydrogen, PDB atom type OH). In the unbound conformation, E283 in TM7 has hydrogen bond interactions with S180 in ECL2. This hydrogen bond is disrupted for AK317 and AK530 bound CCR5.