Figure 2.
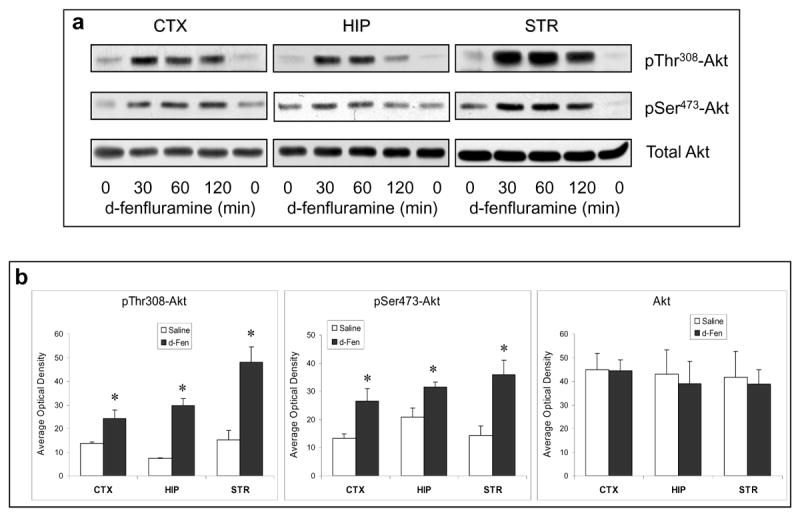
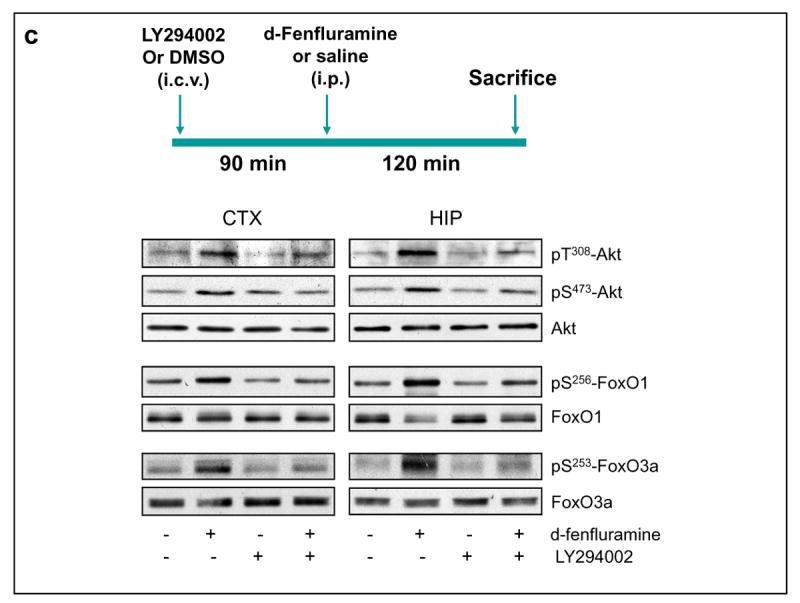
Regulation of Akt signaling pathway by d-fenfluramine. (a) C57BL/6 mice were treated with d-fenfluramine (50 mg/kg, i.p.) before phospho-Thr308-Akt, phospho-Ser473-Akt and total Akt were examined in brain homogenates. (b) Quantification of phospho-Thr308-Akt (t-test; CTX: t=-2.873, p=0.021; HIP: t=-7.842, p=0.001; STR: t=-4.208, p=0.014; n=3-5 per group), phospho-Ser473-Akt (t-test; CTX: t=-2.887, p=0.020; HIP: t=-2.848, p=0.047; STR: t=-3.588, p=0.023; n=3-5 per group), and total Akt after saline and d-fenfluramine (d-Fen) treatment for 2 hr. Data are mean ± SEM. *p<0.05 when values are compared to saline treatment in Student's t-test. (c) Mice received unilateral intra-cerebroventricular (i.c.v.) injection of either LY294002 (5 nM in 1 μl) or DMSO (vehicle, 1 μl) 1.5 hr prior to receiving saline or d-fenfluramine treatment (2 hr). Immunoblots of phosphorylated and total Akt, FoxO1, and FoxO3a are representatives of five separate experiments.
