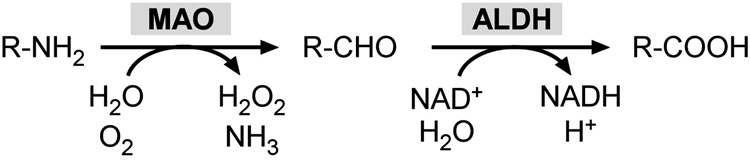
Figure 4. MAO catalyzes the oxidative deamination of monoamines.
Monoamines are degraded by MAO to their correspondent aldehydes (R-CHO). This reaction produces also ammonia (NH3) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Aldehydes are further oxidized by aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) into carboxylic acids (R-COOH). NADH is a critical cofactor for this latter reaction.