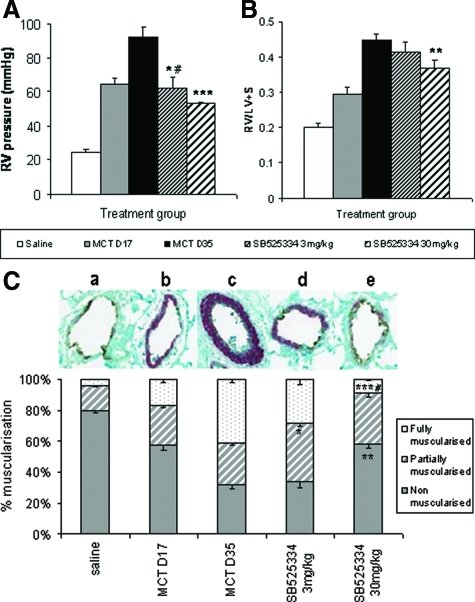
Figure 6.
RV systolic pressure levels (A) and Fulton index measures (RV/LV + S weight ratio) (B) in rats exposed to MCT or saline-negative control. Analysis was performed in rats at the point of established PAH pathology (day 17, gray bars), after which animals were orally treated with either vehicle (black bars), 3 mg/kg (fine hatched bars), or 30 mg/kg (thick hatched bars) SB525334 until day 35. Values are means ± SEM. C: Arteriole remodeling in rats after MCT exposure. Inflated lung sections (n = 10 per group) were stained with vWL and anti-α-smooth muscle actin, and then 200 small vessels (<100 μmol/L) per section were analyzed by an investigator unaware of the source of tissue. Each vessel was assigned as either nonmuscularized (no α-smooth muscle actin staining), partially muscularized, or fully muscularized (thick unbroken wall of smooth muscle), and then the percentage distribution of each calculated per group. A representative picture of the predominantly altered vessel phenotype is provided above each group (a–e). Values are the means ± SEM, #P < 0.05 for MCT day 17 versus vehicle-treated control. *P < 0.01, **P < 0.001, ***P < 0.001 for rct day 35 versus vehicle-treated control (Student’s t-test).