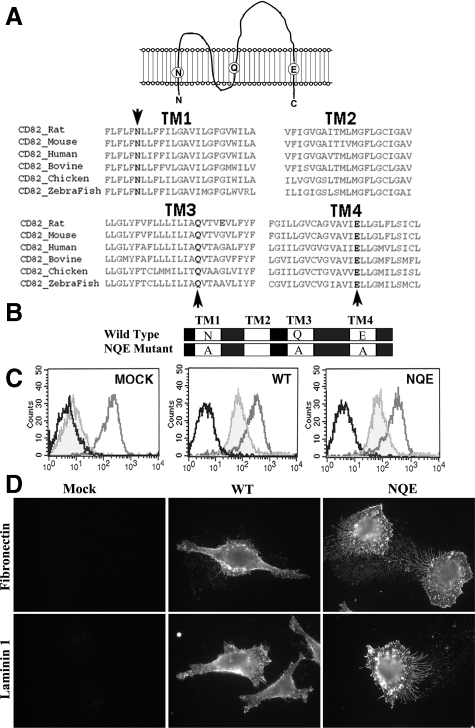
Figure 1.
Schematic presentation of CD82 TM polar residues and establishment of the NQE mutant. A: Sequence alignment of CD82 TM regions. The four TM domains of the vertebrate orthologs of CD82 were aligned by the Clustal W program. Three TM polar residues (in bold and marked with arrow) are fully conserved in all CD82 proteins. B: Schematic presentation of CD82 wild-type and NQE mutant proteins. The NQE mutation denotes that the three conserved TM polar residues, Asn17 (N), Gln99 (Q), and Glu242 (E), are replaced with Ala (A) residues simultaneously. C: Du145 prostate cancer cells were stably transfected with vector (MOCK), CD82 wild-type (WT), and CD82 NQE mutant (NQE). The transfectants were analyzed by flow cytometry for the surface expression of CD82, as shown in light gray. The cells were also stained with a mouse IgG (black) and integrin β1 mAb (medium gray) for negative and positive control, respectively. D: The effect of the NQE mutation on the subcellular distribution of CD82. Du145 transfectant cells cultured on FN (10 μg/ml)- or LN1 (10 μg/ml)-coated glass coverslips were fixed, permeabilized, and incubated with CD82 mAb M104, followed by an FITC-conjugated second Ab incubation. The images were captured under a fluorescent microscope at original magnification ×63.