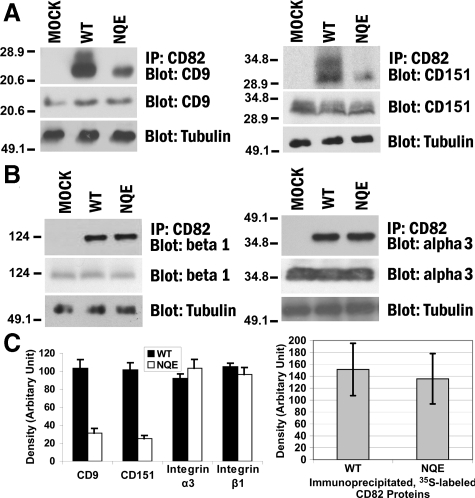
Figure 4.
The TM polar residues are needed for CD82-TEM interaction. A: The NQE mutation diminished CD82-CD9 and -CD151 associations. Du145-Mock, -CD82 WT, and -NQE transfectant cells were lysed in 1% Brij 97, and the lysates were immunoprecipitated with CD82 mAb M104. The precipitates were resolved in nonreducing SDS-PAGE followed by transfer to nitrocellulose membrane. The membrane was blotted with CD9 mAb MAB7 or CD151 mAb 8C3, and the detected proteins were visualized by chemiluminescence. Tubulin, CD9, or CD151 from the same cell lysates was detected by Western blot and used as internal loading controls, respectively. B: The NQE mutation did not alter CD82-β1 and -α3 integrin associations. Cells were lysed in 1% Brij 97, immunoprecipitated with CD82 mAB TS82b, resolved on SDS-PAGE, and transferred to nitrocellulose membrane. The membrane was blotted with integrin β1 mAb TS2/16 or integrin α3 polyclonal antibody D23. Tubulin, integrin β1, or integrin α3 from the same cell lysates was detected in Western blot and used as internal loading controls, respectively. C: Quantification of CD82-associated proteins (left). The tetraspanins and integrins coprecipitated with CD82, as shown in (A) and (B), were quantified by the densitometry analysis of the bands, and the average band densities ± SD from three experiments were plotted as the histogram. Between wild-type and NQE mutant, P values are <0.01 in CD9 and CD151 and >0.05 in integrin α3 and β1 coprecipitations. The comparison of the CD82 protein loading (right). CD82 proteins were immunoprecipitated from an equal number of S35-labeled Du145-CD82 wild-type and NQE transfectant cells and detected by autoradiography after SDS-PAGE separation. The CD82 protein bands were quantified with densitometry analysis, and the average band densities ± SD from three experiments were plotted as the histogram. P > 0.05.