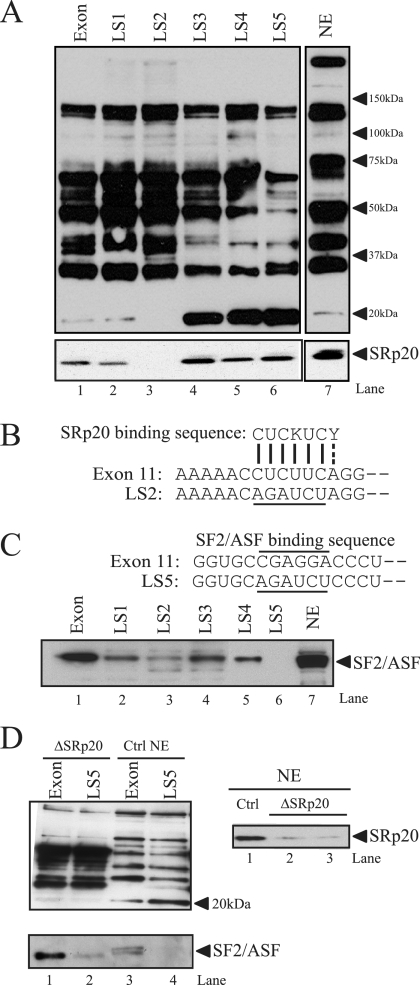
FIG. 2.
SRp20 and SF2/ASF bind to the exon 11 ESE. (A) RNA oligonucleotides corresponding to exon 11 or the LS mutants were covalently linked to adipic acid dihydrazide agarose beads. HeLa nuclear extracts (NE) were incubated with the beads and washed extensively; then, associated proteins were eluted with sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis sample buffer. Bound proteins were separated on 4 to 12% bis-Tris gels and immunoblotted with antibody mAb104 (upper), which recognizes a common phospho-epitope on SR proteins or a monoclonal antibody to SRp20 (lower). NE indicates HeLa nuclear extract (1/25 of input). Representative blots are shown. The experiment was repeated five times, with similar results. (B) Sequence alignment of the exon 11 ESE with the consensus SRp20 binding site. The LS2 mutation (underlined) disrupts this homology. (C) The sequence of the putative SF2/ASF binding site (overlined) and the position of the LS5 linker-scanning mutant (underlined) in exon 11 are indicated (upper). A representative blot shows results for RNA affinity purification of HeLa nuclear proteins followed by immunoblotting with antibodies to SF2/ASF. (D) HeLa nuclear extracts were depleted using antibodies to SRp20, and residual SRp20 levels were determined by Western blotting (right). The same extracts were used for RNA affinity purification and Western blotting with antibody mAb104 (left). The blot was reprobed with anti-SF2/ASF antibodies to check the integrity of other SR proteins in nuclear extract after depletion.