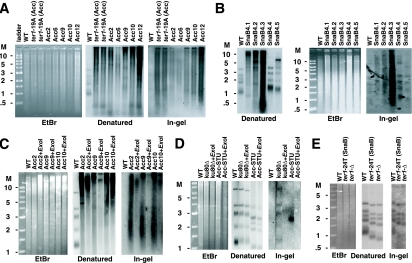
FIG. 6.
Telomeres in Acc and SnaB survivors have substantial amounts of single-stranded DNA. (A) Ethidium bromide-stained gel (EtBr), Southern blot, and in-gel hybridization of DNA from Acc survivors. The first lane in each is a wild-type (WT) control. The second and third lanes are two independent samples of ter1-19A(Acc) cells. The remaining lanes are the same survivors as shown in Fig. 4. (B) Ethidium bromide-stained gel, Southern blot, and in-gel hybridization of EcoRI-digested DNA from each of five streaks of SnaB survivor 4. The streak numbers are noted after the survivor number above the gel. Also shown is the wild-type strain 7B520. The Southern blot and in-gel hybridization only in panel B ran differently and therefore have different size markers. (C) Ethidium bromide-stained gel, Southern blot, and in-gel hybridization of EcoRI-digested and EcoRI- plus Exo I-digested DNAs of Acc survivors 2, 9, 10, and 12 along with those for wild-type strain CBS 2359. Both the Southern blot and in-gel hybridization were probed with a C-stranded telomeric oligonucleotide. (D) Ethidium bromide-stained gel, Southern blot, and in-gel hybridization of EcoRI-digested cells of the wild-type strain CBS 2359 and the EcoRI- and EcoRI- plus Exo I-digested DNAs of ku80Δ cells and senescent ter1-Δ cells containing an Acc-STU telomere that has not yet spread to other telomeres. (E) Ethidium bromide-stained gel, Southern blot, and in-gel hybridization of EcoRI-digested DNAs of the wild-type strain 7B520, a ter1-24T(SnaB) strain, and a ter1-Δ strain. Molecular weight markers (M) are shown in kilobases.