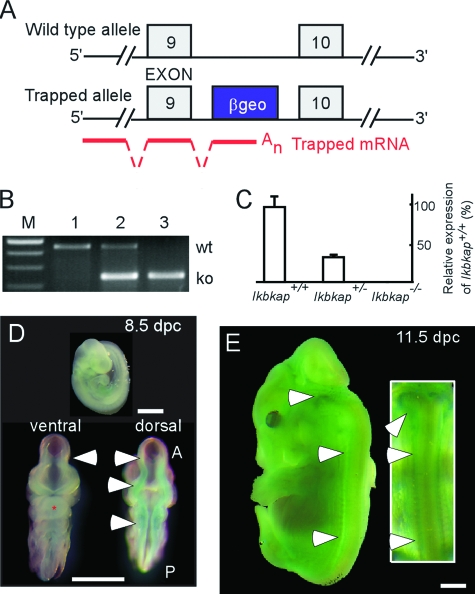
FIG. 1.
Gene targeting strategy and Ikbkap expression. (A) Schematic of the wild-type and knockout Ikbkap alleles. The blue cassette (β-geo) represents the vector containing β-galactosidase, neomycin phosphotransferase II, and stop codons that is inserted into intron 9. The insertion creates a fusion transcript containing the exons upstream of the insertion joined to the β-geo marker, as illustrated by the red lines. (B) PCR genotyping results of genomic DNA from embryonic day 9.5 samples. Lanes 1, 2, and 3 represent the wild-type (Ikbkap+/+), heterozygous (Ikbkap+/−), and homozygous (Ikbkap−/−) genotypes, respectively. wt, wild-type fragment (454 bp); ko, knockout fragment (244 bp). (C) The relative amounts of Ikbkap transcripts expressed in embryos with different genotypes at 8.5 dpc as demonstrated by quantitative RT-PCR. The error bars indicate standard deviations. (D and E) X-Gal staining of whole-mount Ikbkap+/− embryos at 8.5 and 11.5 dpc, respectively. The arrowheads in panel D point to the ventral and dorsal neural tubes; note that the primitive hindbrain region shows higher positive reactivity. The arrowheads in panel E point to the hindbrain and dorsal ganglia. A, anterior; P, posterior. Scale bars, 1 mm.