Figure 7.
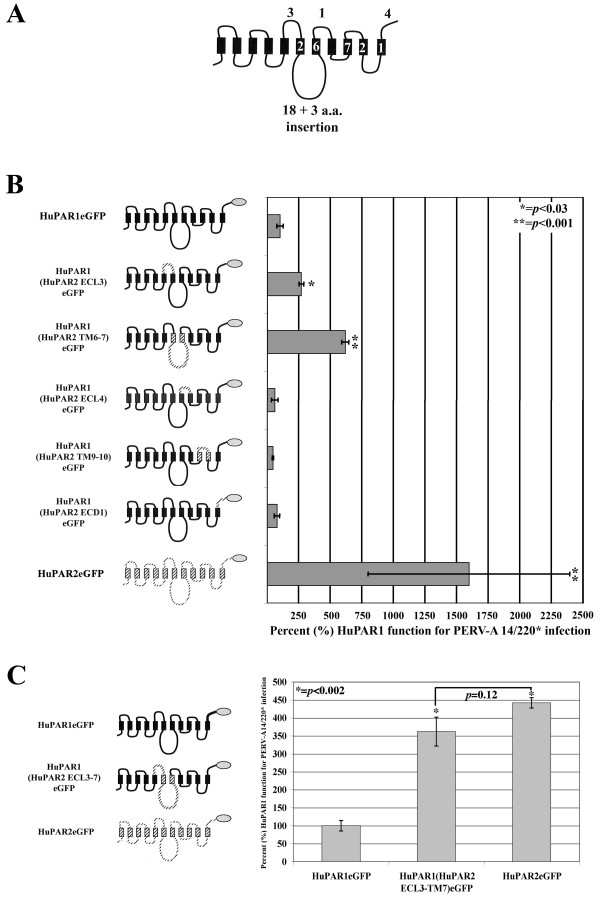
Finer mapping of HuPAR2 residues 170–448 reveal that extracellular loop 3 (ECL3), and the region spanning transmembrane domain 6 and 7 (TM6–7), contribute to the increased function. (A) shows the number of single amino acid differences for each structural region in the current topology model. (B) shows the eGFP-tagged chimeras (gray oval) constructed between HuPAR1 (solid) and HuPAR2 (dashed) used for mapping [transmembrane (TM), extracellular loop (ECL), intracellular loop (ICL), extracellular domain (ECD)]. Statistically significant increases were seen for ECL3 (p ≤ 0.03) and TM6–7 (p ≤ 0.001), implicating these regions as contributing to the increased functional efficiency of HuPAR2. (C) shows a statistically significant (p < 0.002) increase for infection, essentially to HuPAR2 wild-type levels, for the ECL3-TM7-containing chimera.