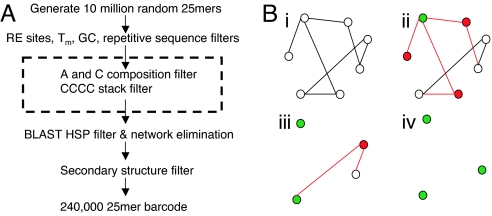
Fig. 1.
The DeLOB DNA barcode design procedure. (A) Ten million random 25mers were generated and sequentially passed through restriction enzyme (RE) site, Tm, GC composition, and repetitive sequence filters. Candidates passing these filters were searched against themselves by BLAST and a subset of orthogonal sequences was selected on the basis of their BLAST results and the network elimination algorithm. After applying a secondary structure filter to eliminate self-folding-prone candidates, we obtained a final set of 240,000 probes. The 2 filters in the dashed box were based on rules discovered from analyzing hybridization data from first round probe design. (B) The network elimination algorithm. (i) Nonorthogonal candidate pairs were represented by a network graph. Each vertex was a candidate and each edge was a longer than 12-base match between the 2 connected candidates. (ii) One candidate was randomly chosen and placed in the orthogonal group (green). All candidates that were connected to this one were labeled in red and then eliminated from the network together with all edges incident to these red vertices. (iii) The random selection and elimination steps were repeated on the remaining network members. (iv) At the end, only orthogonal candidates were left.